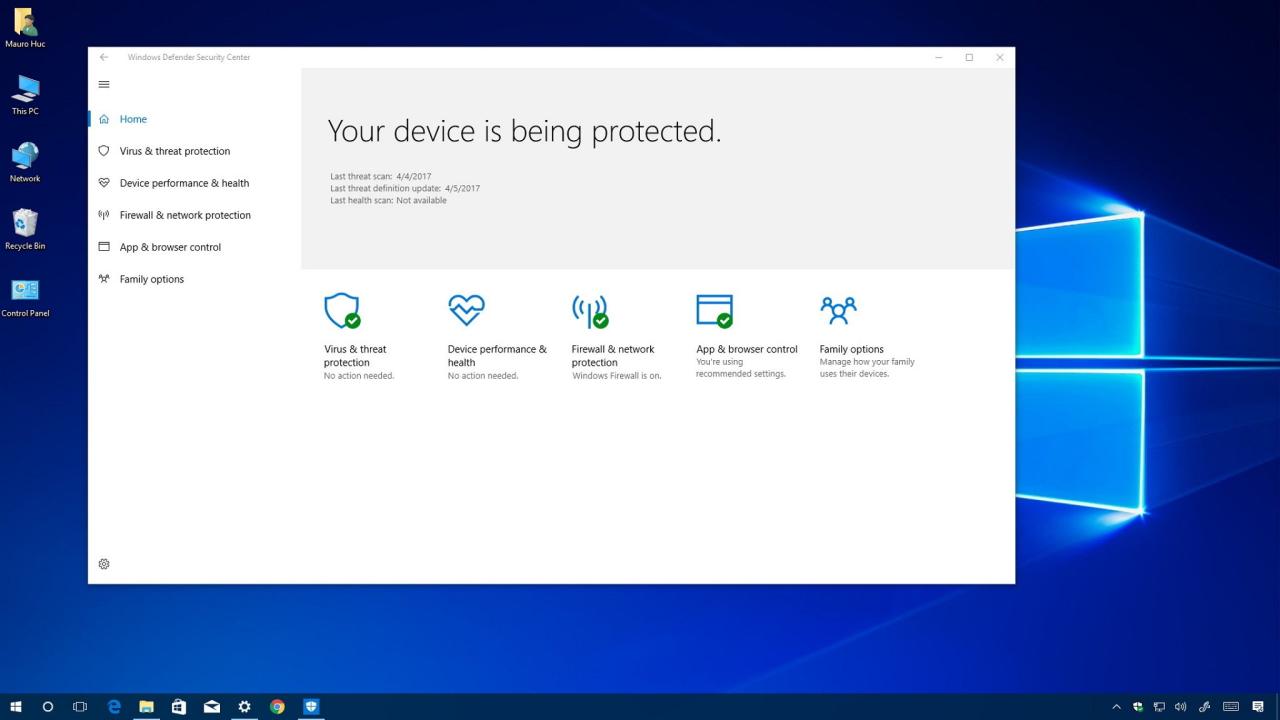
Windows Defender, your system’s built-in security champion, stands guard against a relentless onslaught of digital threats. It’s a silent guardian, constantly working behind the scenes to keep your data safe and your system secure. This digital warrior has evolved over the years, adapting to the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.
Table of Contents
From its humble beginnings as a basic antivirus solution, Windows Defender has become a comprehensive security suite, offering real-time protection, antivirus scanning, firewall, and more. Its arsenal includes advanced technologies like signature-based detection and behavioral analysis, allowing it to identify and neutralize even the most sophisticated malware.
Introduction to Windows Defender
Windows Defender is an essential security solution that plays a crucial role in safeguarding your Windows device from various threats, including malware, viruses, and ransomware. It’s a built-in security feature that offers real-time protection against potential threats, ensuring your system remains secure and operational.
History and Evolution
Windows Defender has a long history, evolving alongside Windows operating systems. Initially introduced as Windows AntiSpyware in 2006, it was later renamed to Microsoft Security Essentials in 2009. The name Windows Defender was reintroduced in 2012 with Windows 8, marking a significant upgrade and integration with Windows security features. Over time, Windows Defender has continuously been enhanced with new features and capabilities, becoming a robust and comprehensive security solution.
Key Features and Functionalities
Windows Defender offers a wide range of features and functionalities to protect your device:
- Real-time Protection: Windows Defender constantly monitors your system for suspicious activity and blocks potential threats before they can harm your device. This proactive approach ensures continuous protection against malware and other malicious software.
- Virus and Malware Scanning: Windows Defender performs regular scans of your system to detect and remove existing threats. You can also initiate manual scans at any time to ensure your device is free from malware.
- Firewall Protection: Windows Defender Firewall acts as a barrier between your device and the internet, blocking unauthorized access and preventing malicious connections. It filters incoming and outgoing network traffic, protecting your system from potential attacks.
- Phishing and Exploit Protection: Windows Defender safeguards you from phishing attempts and exploits by identifying and blocking malicious websites and files. It analyzes websites and files for suspicious content, preventing you from falling victim to online scams and attacks.
- Application Control: Windows Defender allows you to control which applications can run on your device. You can create rules to block or allow specific applications, enhancing your security by preventing potentially harmful software from executing.
- Automatic Updates: Windows Defender automatically updates itself to ensure you have the latest protection against emerging threats. These regular updates provide new security definitions and enhance its capabilities to combat the latest malware and viruses.
Protection Mechanisms
Windows Defender employs a multifaceted approach to safeguard your system from malicious threats. It integrates various protection mechanisms, including real-time monitoring, antivirus scanning, and a robust firewall, to detect and neutralize potential dangers. These mechanisms work in conjunction with advanced technologies for threat detection, such as signature-based detection and behavioral analysis, to ensure comprehensive protection.
Real-Time Protection
Real-time protection is a crucial aspect of Windows Defender’s security strategy. It continuously monitors your system for suspicious activities and potential threats. This constant vigilance helps to prevent malicious software from gaining access to your device and executing harmful actions. Windows Defender’s real-time protection operates in the background, scanning files, applications, and websites as you interact with them. It leverages a combination of signature-based detection and behavioral analysis to identify known and unknown threats.
Antivirus Scanning
Windows Defender performs regular antivirus scans to identify and remove malware from your system. These scans can be scheduled at specific intervals or triggered manually. During an antivirus scan, Windows Defender analyzes files and system processes to detect any signs of malicious activity. It uses a database of known malware signatures to identify threats. If suspicious files are found, Windows Defender will quarantine or remove them to prevent further damage.
Firewall
The Windows Defender Firewall acts as a barrier between your computer and the external network. It controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized connections and preventing malicious actors from accessing your system. The firewall analyzes network traffic based on predefined rules and blocks any communication that is deemed suspicious or potentially harmful. It helps to protect your system from attacks like hacking attempts, denial-of-service attacks, and malware infections.
Threat Detection Technologies
Windows Defender employs a variety of threat detection technologies to identify and neutralize malicious threats. These technologies include:
- Signature-Based Detection: This method relies on a database of known malware signatures. When Windows Defender encounters a file that matches a known malware signature, it flags it as malicious and takes appropriate action. Signature-based detection is effective against known threats, but it may struggle to detect new or previously unseen malware.
- Behavioral Analysis: Behavioral analysis focuses on identifying suspicious patterns in software behavior. Windows Defender monitors the actions of running applications and identifies any deviations from normal behavior. This helps to detect malware that may not have a known signature or that uses obfuscation techniques to evade detection.
Interaction with Other Security Software
Windows Defender is designed to work seamlessly with other security software installed on your system. It uses a mechanism called “anti-malware platform” (AMP) to coordinate with other security solutions. This allows Windows Defender to share threat information and collaborate with other security products to provide a more comprehensive layer of protection.
Antivirus and Malware Protection

Windows Defender is an integral part of Windows security, offering robust protection against various malware threats. It constantly monitors your system for suspicious activity and proactively defends against potential attacks.
Types of Malware Threats Detected and Removed
Windows Defender is designed to detect and remove a wide range of malware threats, including:
- Viruses: These malicious programs can replicate themselves and spread to other files, causing damage to your system.
- Worms: Worms are self-replicating programs that can spread across networks without user interaction.
- Trojan horses: These programs disguise themselves as legitimate software but contain malicious code that can steal your data or compromise your system.
- Spyware: Spyware collects information about your online activity and sends it to third parties without your consent.
- Adware: Adware displays unwanted advertisements on your computer, often without your permission.
- Ransomware: Ransomware encrypts your files and demands payment for their decryption.
- Rootkits: Rootkits are designed to hide malicious software from detection by security programs.
- Exploits: Exploits take advantage of vulnerabilities in software to gain unauthorized access to your system.
Effectiveness of Windows Defender Compared to Other Antivirus Solutions
Windows Defender provides a solid level of protection against common malware threats and is generally considered effective for everyday users. However, its effectiveness can vary depending on the specific malware and the user’s security practices.
Some independent testing labs, like AV-TEST and AV-Comparatives, have consistently ranked Windows Defender as a top performer, with high detection rates and minimal impact on system performance.
However, it’s important to note that specialized antivirus solutions may offer more comprehensive protection, especially for users who are at higher risk of malware infection.
Limitations of Windows Defender
While Windows Defender offers good protection, it has some limitations:
- Limited customization: Windows Defender provides fewer customization options compared to some third-party antivirus solutions, making it less flexible for advanced users.
- Potential for false positives: Like any antivirus software, Windows Defender can sometimes flag legitimate files as malware, resulting in false positives.
- Limited real-time protection: Windows Defender’s real-time protection may not be as robust as some third-party solutions, potentially leaving your system vulnerable to certain types of malware.
- Limited support for specific malware types: While Windows Defender is effective against many common malware threats, it may not be as effective against emerging or highly sophisticated malware types.
Firewall and Network Security

Windows Defender Firewall is a crucial component of Windows security, acting as a barrier between your computer and the outside world. It meticulously examines incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking potentially harmful connections while allowing safe ones to pass through. This intelligent filter plays a vital role in safeguarding your system from various cyber threats, such as malicious software, hackers, and unauthorized access attempts.
Firewall Rules and Settings
Windows Defender Firewall offers a comprehensive set of rules and settings that allow you to fine-tune its behavior and control which applications and services are allowed to communicate with the internet. These rules can be configured based on specific criteria, such as the application’s name, the port it uses, the source and destination IP addresses, and the protocol (e.g., TCP, UDP).
- Inbound Rules: These rules determine which applications and services are allowed to receive connections from the internet. For instance, you might allow your web browser to receive incoming connections on port 80 (HTTP) while blocking all other applications from receiving connections on that port.
- Outbound Rules: These rules govern which applications and services are allowed to initiate connections to the internet. For example, you could block a specific application from connecting to a particular website or restrict all applications from accessing the internet except for your web browser and email client.
- Advanced Settings: Windows Defender Firewall provides advanced settings that allow you to configure firewall behavior in greater detail. These settings include the ability to create custom rules, manage firewall profiles for different network locations (e.g., home, work, public), and enable or disable firewall features.
Impact of Firewall Rules
Firewall rules can have a significant impact on network connectivity and performance.
- Restricted Connectivity: Overly restrictive firewall rules can prevent legitimate applications from accessing the internet or communicating with other devices on your network. This can lead to issues with browsing the web, accessing online services, or connecting to shared resources.
- Performance Impact: Firewall rules can impact network performance, especially when dealing with large amounts of traffic. If the firewall is configured to inspect every packet of data, it can introduce latency and slow down network operations. This is more likely to be noticeable on older or less powerful computers.
Security Updates and Patches
Keeping your operating system and security software up-to-date is crucial for maintaining a secure computing environment. Windows Defender, being an integral part of Windows security, is constantly evolving to address emerging threats.
Importance of Security Updates
Security updates, also known as patches, are essential for addressing vulnerabilities and security flaws that could be exploited by malicious actors. These updates often include fixes for bugs, improvements to system performance, and enhancements to security features.
- Protection Against New Threats: Security updates introduce new defenses against newly discovered malware, viruses, and other threats. These updates often include updated definitions for antivirus engines, allowing them to identify and neutralize new attacks.
- Vulnerability Patching: Security updates patch known vulnerabilities in the operating system and software applications. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to your system, steal data, or install malware.
- Enhanced Security Features: Updates often include enhancements to existing security features or introduce new security mechanisms to strengthen system protection. These enhancements might involve improvements to firewall rules, intrusion detection systems, or data encryption capabilities.
Windows Defender and Windows Update Integration
Windows Defender seamlessly integrates with Windows Update, ensuring that your system receives the latest security updates automatically. This integration streamlines the update process, making it easier for users to keep their systems secure.
- Automatic Updates: By default, Windows Update is configured to automatically download and install critical security updates. This ensures that your system is protected against the latest threats without requiring manual intervention.
- Scheduled Updates: You can also configure Windows Update to download and install updates at specific times, allowing you to control the update process and minimize potential disruptions to your workflow.
- Update Notifications: Windows Update will notify you when security updates are available, providing you with the opportunity to review and install them at your convenience.
Impact of Outdated Software
Using outdated software can significantly compromise system security. Outdated software is more vulnerable to attacks, as it lacks the latest security patches and defenses.
- Exploitable Vulnerabilities: Outdated software often contains known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to your system, steal data, or install malware.
- Lack of Security Updates: Outdated software does not receive security updates, leaving it exposed to new threats and vulnerabilities.
- Compatibility Issues: Outdated software can lead to compatibility issues with other applications and operating systems, potentially affecting system performance and stability.
Closure
Windows Defender is your first line of defense, a powerful tool that can significantly enhance your system’s security. While it may not be a perfect solution, it offers a solid foundation for protecting your digital world. By staying informed about its features, limitations, and best practices, you can leverage its capabilities to safeguard your data and maintain peace of mind in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Windows Defender is a reliable tool for keeping your computer safe from malware, but it can sometimes be a bit intrusive, especially if you’re working on a project that requires a lot of focus. If you find yourself constantly getting distracted by pop-ups or notifications, you might want to consider using a time management tool like time doctor to help you stay on track.
While Windows Defender can be a great first line of defense, it’s always good to have additional tools in your arsenal to help you stay productive and focused.
