GarageBand, Apple’s intuitive music creation software, has revolutionized the way people make music. Whether you’re a seasoned musician or a curious beginner, GarageBand provides a comprehensive platform to explore your creativity and bring your musical ideas to life. From recording instruments and vocals to crafting elaborate MIDI sequences, GarageBand offers a user-friendly interface and powerful tools for every stage of the music production process.
Table of Contents
With a vast library of instruments, sounds, and effects, GarageBand empowers users to experiment with different genres and styles, pushing the boundaries of their musical imagination. Whether you’re composing original songs, remixing existing tracks, or simply exploring the world of music production, GarageBand provides a rich and engaging environment for musical exploration.
GarageBand Overview
GarageBand is a powerful and versatile digital audio workstation (DAW) developed by Apple Inc. It has been a staple in the Mac ecosystem for over two decades, empowering individuals of all skill levels to create music, podcasts, and other audio projects.
History and Evolution
GarageBand’s journey began in 2004 as a simple yet effective music creation tool for Mac users. Initially, it was designed to be a user-friendly introduction to music production, offering a streamlined interface and a collection of built-in instruments and loops. Over the years, GarageBand has undergone significant transformations, expanding its feature set and capabilities to cater to a wider range of users.
- Early Years (2004-2010): GarageBand’s initial focus was on providing a simple and accessible way for beginners to create music. It offered a limited selection of instruments, loops, and effects, but it was praised for its intuitive interface and ease of use.
- Expansion and Refinement (2010-2020): As technology advanced, GarageBand evolved to include more advanced features, such as support for external MIDI controllers, improved audio editing tools, and a wider range of instruments and effects. It also saw the introduction of features like Drummer, a virtual drummer that could generate realistic drum tracks, and Smart Controls, which allowed users to manipulate multiple parameters with a single control.
- Modern GarageBand (2020-Present): In recent years, GarageBand has continued to evolve, with a focus on enhancing its collaboration features, expanding its library of sounds and instruments, and integrating with other Apple services. It now includes features like Live Loops, a grid-based sequencer that allows users to easily arrange and experiment with different musical ideas, and Sound Library, a vast collection of sounds and instruments that can be accessed through iCloud.
Key Features and Functionalities, Garageband
GarageBand offers a comprehensive set of tools and features for music creation, podcasting, and audio editing. Some of its key features include:
- Virtual Instruments: GarageBand comes with a wide range of virtual instruments, including pianos, guitars, drums, synthesizers, and more. These instruments are designed to sound realistic and offer a variety of customization options.
- Audio Recording: GarageBand allows users to record audio directly into the software using a microphone or an external audio interface. It provides features for editing, mixing, and mastering audio tracks.
- Loops and Samples: GarageBand includes a vast library of loops and samples that can be used to create music and soundtracks. These loops are categorized by genre and tempo, making it easy to find the right sounds for your project.
- Effects and Plugins: GarageBand offers a range of built-in effects and plugins that can be used to enhance audio tracks. These include EQs, compressors, delays, reverbs, and more.
- Collaboration Features: GarageBand allows users to collaborate on projects with others, even if they are not in the same location. Users can share projects with others, and they can work on the same project simultaneously.
- Sound Library: GarageBand’s Sound Library provides access to a vast collection of sounds, instruments, and loops that can be used in projects. The Sound Library is constantly being updated with new content.
- Live Loops: Live Loops is a grid-based sequencer that allows users to easily arrange and experiment with different musical ideas. It provides a visual representation of the project, making it easy to see and manipulate different parts of the song.
Target Audience and User Base
GarageBand caters to a diverse audience, from aspiring musicians and hobbyists to seasoned professionals. It has become a popular choice for:
- Beginners: GarageBand’s intuitive interface and comprehensive tutorials make it an ideal starting point for individuals who are new to music production.
- Hobbyists and Enthusiasts: GarageBand provides a powerful and flexible platform for hobbyists and enthusiasts to explore their creativity and create music for personal enjoyment or sharing with friends and family.
- Students: GarageBand is widely used in educational settings, providing students with a hands-on learning experience in music production and audio engineering.
- Podcasters: GarageBand’s audio editing tools and features make it a suitable platform for recording and editing podcasts.
- Independent Artists: GarageBand has become a popular choice for independent artists and musicians who are looking for a cost-effective and user-friendly way to produce and release their music.
GarageBand Interface and Workflow
GarageBand’s user interface is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced musicians. The interface is divided into various sections, each serving a specific purpose in the music creation process. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of the GarageBand interface and its components, along with a step-by-step guide on how to create music using GarageBand.
GarageBand Interface Overview
The GarageBand interface is divided into several key areas, each contributing to the overall functionality of the application.
- Track List: The Track List displays all the audio and MIDI tracks in your project. You can add, delete, and arrange tracks here.
- Main Toolbar: The Main Toolbar, located at the top of the window, provides access to various essential features like recording, playback, and editing.
- Transport Controls: These controls, found within the Main Toolbar, allow you to start, stop, rewind, and fast-forward playback.
- Control Bar: The Control Bar, positioned below the Track List, provides access to various controls for adjusting track volume, panning, and other parameters.
- Piano Roll Editor: This editor allows you to edit MIDI data, including notes, velocity, and timing.
- Audio Track Editor: The Audio Track Editor is used for editing audio recordings, including trimming, cutting, and applying effects.
- Inspector: The Inspector provides detailed information about the selected track or instrument. It allows you to adjust settings like instrument parameters, effects, and automation.
Workflow for Creating Music in GarageBand
The workflow for creating music in GarageBand typically involves several key steps:
- Project Setup: Start by creating a new project. Choose a template based on your desired genre or instrument.
- Adding Tracks: Add audio or MIDI tracks to your project. You can use the built-in instruments, import your own audio files, or record live audio.
- Recording: Record audio or MIDI data using the built-in instruments or external microphones.
- Editing: Edit your recordings using the various tools available in GarageBand. This includes trimming, cutting, and applying effects.
- Arranging: Arrange your tracks by moving, copying, and pasting them in the timeline. You can also use the loop browser to add pre-recorded loops and samples.
- Mixing: Mix your tracks by adjusting volume, panning, and other parameters. You can also add effects like reverb, delay, and equalization.
- Mastering: Master your project by adjusting the overall volume, EQ, and dynamics.
- Exporting: Export your finished project in various formats, including MP3, WAV, and AIFF.
Using Instruments and Loops
GarageBand provides a wide selection of virtual instruments and loops to enhance your music production.
- Virtual Instruments: GarageBand offers a diverse collection of virtual instruments, including pianos, guitars, drums, and synthesizers.
- Loop Browser: The Loop Browser allows you to browse and add pre-recorded loops and samples to your project.
Adding and Editing Audio
GarageBand enables you to import and edit audio files seamlessly.
- Importing Audio: You can import audio files from your computer or other devices into GarageBand.
- Editing Audio: GarageBand provides a variety of tools for editing audio, including trimming, cutting, and applying effects.
Adding and Editing MIDI
MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a protocol that allows you to control and record musical information. GarageBand supports MIDI input and editing.
- MIDI Input: You can connect a MIDI keyboard or other MIDI controllers to GarageBand to record MIDI data.
- MIDI Editing: The Piano Roll Editor in GarageBand allows you to edit MIDI data, including notes, velocity, and timing.
Adding and Editing Effects
Effects can be used to enhance the sound of your tracks.
- Audio Effects: GarageBand offers a wide range of audio effects, including reverb, delay, equalization, and distortion.
- MIDI Effects: MIDI effects can be used to modify the sound of MIDI instruments.
Using the Inspector
The Inspector provides detailed information about the selected track or instrument.
- Track Settings: The Inspector allows you to adjust track settings like volume, panning, and effects.
- Instrument Settings: For instruments, the Inspector provides access to various parameters, such as tuning, timbre, and articulation.
Audio Recording and Editing
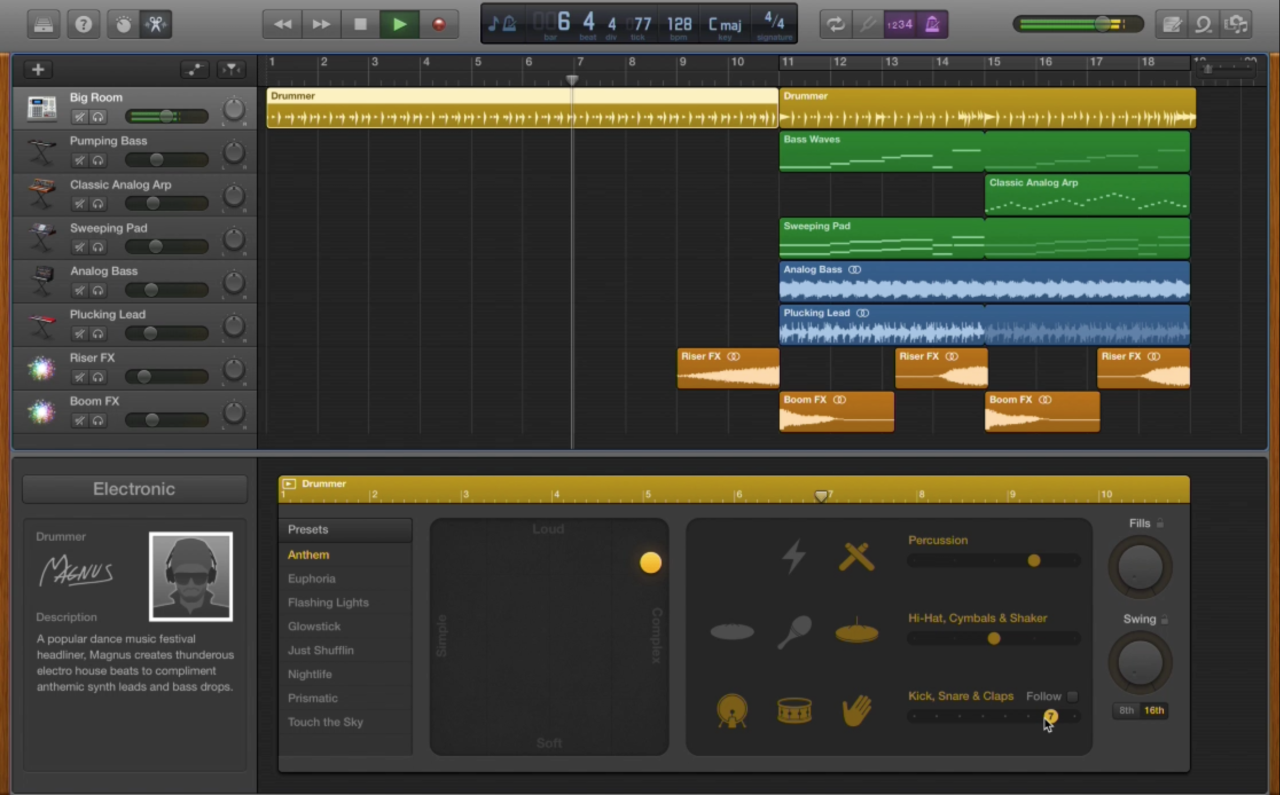
GarageBand provides a user-friendly environment for recording and editing audio, whether you’re a seasoned musician or just starting out. It offers a range of tools and features to capture your musical ideas and transform them into polished tracks.
Recording Audio
GarageBand makes it easy to record audio using a variety of input sources, including microphones, instruments, and even external audio devices. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to record audio in GarageBand:
1. Select a Track: Choose the type of track you want to record, such as an audio track, a software instrument track, or an external instrument track.
2. Choose an Input Source: Select the input source you’ll be using for recording, such as a microphone, an instrument, or an external audio device.
3. Adjust Recording Settings: Customize the recording settings, including the sample rate, bit depth, and input level.
4. Press the Record Button: Once you’re ready, click the red record button to begin recording.
5. Monitor the Recording: As you record, monitor the audio levels to ensure you’re getting a clear and balanced signal.
6. Stop Recording: When you’re finished recording, click the stop button to end the recording session.
Recording Options and Settings
GarageBand provides several recording options and settings to help you capture the best possible audio.
* Input Level: Adjust the input level to ensure a clear signal without clipping or distortion.
* Monitoring: You can choose between direct monitoring (hearing the input signal directly) and software monitoring (hearing the signal after it’s processed by GarageBand).
* Looping: You can enable looping to record multiple takes of a section of audio.
* Quantization: This feature allows you to align your recorded audio to the beat of the track.
* Audio Effects: Apply real-time audio effects during recording to enhance the sound of your performance.
Audio Editing Tools and Techniques
GarageBand offers a wide array of tools and techniques to edit your recorded audio.
* Trim and Split: Use the trim tool to remove unwanted sections of audio and the split tool to divide a track into multiple regions.
* Cut, Copy, and Paste: Cut, copy, and paste audio regions to rearrange them within a track or move them to different tracks.
* Fade In/Out: Use fade-in and fade-out tools to smoothly transition between audio regions.
* Crossfades: Create seamless transitions between audio regions by using crossfades.
* Quantization: Align recorded audio to the beat of the track.
* Audio Effects: Apply a variety of audio effects, such as reverb, delay, equalization, and compression.
* Automation: Automate track parameters, such as volume, panning, and effects, over time.
* MIDI Editing: Edit MIDI data, such as notes, velocities, and timing.
Instruments and Sounds
GarageBand comes with a vast library of instruments and sounds, ready to fuel your musical creativity. You can find everything from classic instruments like guitars, drums, and pianos to more unique sounds like synthesizers, orchestral instruments, and even sound effects. Let’s dive into how to use and customize these instruments and sounds to create your musical masterpiece.
Using and Customizing Instruments and Sounds
GarageBand provides a user-friendly interface for exploring and using its instruments and sounds.
- Instrument Browser: To access the Instrument Browser, click on the “Add Track” button at the bottom of the GarageBand window. You can then browse through different categories of instruments like “Guitar,” “Piano,” “Drums,” “Synths,” and “World.”
- Sound Library: Each instrument has a library of different sounds or presets. To explore these, click on the instrument icon in the track header. You can scroll through the list of sounds or use the search bar to find specific sounds.
- Customization: Many instruments in GarageBand offer customization options. You can adjust the sound’s tone, volume, effects, and even create your own unique sounds using the instrument’s built-in editor.
Importing External Audio Files
While GarageBand provides a vast library of instruments and sounds, you can also import your own external audio files to enrich your projects.
- Drag and Drop: The simplest way to import external audio files is by dragging and dropping them directly onto the GarageBand window. You can import audio files from your computer’s hard drive or external storage devices.
- File Menu: You can also import audio files by going to the “File” menu and selecting “Import.” This opens a file dialog where you can choose the audio file you want to import.
- Audio Track: Once imported, the audio file will appear on a new Audio track in GarageBand. You can then edit and manipulate the audio file using the various editing tools available in GarageBand.
MIDI and Sequencing
MIDI, or Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a language that allows electronic musical instruments and computers to communicate with each other. It doesn’t transmit actual audio, but rather instructions that tell instruments how to play notes, change sounds, and control various parameters. This makes it a powerful tool for music production, as it allows you to create and manipulate musical ideas without needing to record actual audio.
Using MIDI Instruments and Sequencers
MIDI instruments are devices that can be controlled using MIDI data. This includes keyboards, drum machines, and even specialized controllers that allow you to manipulate parameters like volume, pitch, and effects. GarageBand includes a variety of virtual MIDI instruments, such as pianos, synthesizers, and drum kits, that can be used to create and edit MIDI tracks.
GarageBand’s sequencer allows you to arrange and edit MIDI data. It uses a piano roll interface where you can draw in notes and control their timing, velocity, and other parameters. This allows you to create complex melodies, rhythms, and harmonies with great precision.
Creating and Editing MIDI Tracks
Creating a MIDI track in GarageBand is simple. You can select a MIDI instrument from the library and drag it onto the timeline. Then, you can use the sequencer to record your musical ideas. The sequencer displays a grid that represents the musical timeline, and you can click or drag notes into the grid to create your melody or rhythm.
Once you’ve recorded a MIDI track, you can edit it in various ways. You can adjust the timing, velocity, and pitch of individual notes, as well as apply effects and other modifications. This allows you to fine-tune your musical ideas and create unique and expressive performances.
Key Features of MIDI Sequencing in GarageBand
- Piano Roll: The piano roll is the primary tool for editing MIDI data in GarageBand. It allows you to visually edit notes, change their timing, velocity, and other parameters.
- Quantization: This feature helps to improve the timing of your MIDI performances by snapping notes to the nearest grid position.
- MIDI Controllers: GarageBand supports a wide range of MIDI controllers, allowing you to control instruments and parameters in real-time.
- Automation: You can automate various parameters, such as volume, pan, and effects, to create dynamic and expressive performances.
Effects and Processing
Effects and processing are essential for shaping and enhancing the sound of your music in GarageBand. They allow you to add depth, texture, and character to your audio tracks, transforming your recordings from raw to polished. You can explore a wide range of built-in effects, ranging from subtle enhancements to dramatic transformations, to create a unique sonic landscape for your tracks.
Built-in Audio Effects
GarageBand offers a comprehensive collection of built-in audio effects, categorized into various types.
- Amplifier: Simulates the sound of various guitar amplifiers, allowing you to dial in different tones and textures for your electric guitar recordings.
- Compressor: Controls the dynamic range of your audio, making quieter parts louder and louder parts softer. This can help even out the volume of a track and create a more consistent sound.
- Delay: Creates echoes and repetitions of your audio signal, adding depth and space to your tracks. You can adjust the delay time, feedback, and other parameters to create different delay effects.
- EQ: Allows you to adjust the frequency content of your audio, boosting or cutting specific frequencies to shape the sound of your track.
- Filter: Filters out specific frequencies from your audio, allowing you to shape the sound of your track in different ways. You can create high-pass, low-pass, band-pass, and other types of filters.
- Phaser: Creates a swirling, psychedelic effect by shifting the phase of your audio signal.
- Reverb: Simulates the sound of a room or space, adding depth and realism to your recordings. You can choose from various reverb types, such as hall, room, plate, and spring.
- Stereo Imager: Adjusts the stereo width of your audio, making it sound wider or narrower.
- Vocal Transformer: Allows you to manipulate the sound of your vocals, adding effects like pitch correction, harmonization, and vocal doubling.
Applying and Customizing Effects
Applying and customizing effects in GarageBand is straightforward.
- Select the audio track to which you want to apply an effect.
- Click the “Effects” button in the track header.
- Browse the list of effects and select the one you want to apply.
- Adjust the effect parameters to your liking. Each effect has its own set of parameters that you can customize to achieve the desired sound.
- Experiment with different effects and settings to discover the sounds that work best for your music.
Creating and Using Custom Audio Effects
GarageBand allows you to create and use your own custom audio effects using the “Audio Unit” format.
Custom Audio Units are plug-ins that can be used in GarageBand and other audio software to create unique and specialized effects.
You can find a wide variety of free and paid custom audio units online.
- Download and install the custom audio unit you want to use.
- Open GarageBand and select the audio track to which you want to apply the effect.
- Click the “Effects” button in the track header.
- Select the “Audio Units” category and choose the custom audio unit you installed.
- Adjust the effect parameters to your liking.
Mixing and Mastering
Mixing and mastering are essential steps in the audio production process, ensuring your tracks sound polished and professional. Mixing involves balancing and adjusting the individual audio tracks within your song, creating a cohesive and well-defined sound. Mastering takes the final mixed track and optimizes it for various listening environments, enhancing its overall loudness and clarity.
Mixing Tools in GarageBand
GarageBand offers a comprehensive suite of mixing tools to help you achieve the desired sound for your music.
- Channel Strip: The channel strip is the primary tool for mixing individual tracks. It provides a range of controls, including volume, pan, EQ, and effects, allowing you to shape and adjust each track’s sound.
- EQ: Equalizers (EQs) are used to adjust the frequency content of individual tracks, boosting or cutting specific frequencies to enhance clarity, remove unwanted noise, or create a desired tonal balance.
- Compressor: Compressors even out the dynamic range of a track, reducing the difference between the loudest and quietest parts. This creates a more consistent and punchier sound.
- Reverb: Reverb adds a sense of space and depth to a track, simulating the reflections of sound in a real-world environment.
- Delay: Delay creates echoes and repeats of a sound, adding rhythmic interest and texture to a track.
- Automation: GarageBand allows you to automate various parameters, including volume, pan, and effects, over time. This enables you to create dynamic changes and transitions in your mix.
Mastering Tools in GarageBand
GarageBand offers tools to master your final mix, ensuring it sounds loud, clear, and ready for distribution.
- Mastering Channel Strip: The mastering channel strip provides a dedicated set of tools for mastering, including EQ, limiter, and multiband compressor.
- Limiter: Limiters are used to prevent audio signals from exceeding a specific volume level, ensuring that the track is loud without distortion.
- Multiband Compressor: Multiband compressors allow you to compress different frequency ranges independently, offering more control over the dynamics of the track.
Mixing and Mastering a Track in GarageBand
Mixing and mastering a track in GarageBand involves a series of steps to achieve a polished and professional sound.
- Prepare Your Track: Start by ensuring your track is properly organized and ready for mixing. This includes grouping related tracks, assigning them to separate buses, and making sure all instruments and vocals are recorded at a reasonable volume.
- Basic Mixing: Begin by adjusting the volume and pan of each track. This will help you create a balanced and well-defined stereo image. Use EQ to remove unwanted frequencies, such as muddiness in the low end or harshness in the high end.
- Add Effects: Experiment with effects like reverb, delay, and compression to enhance the sound of individual tracks and create a sense of space and depth. Remember to use effects sparingly and tastefully.
- Mastering: Once your mix is complete, move to the mastering stage. Use the mastering channel strip to apply a gentle EQ to enhance the overall frequency balance. Use a limiter to maximize the loudness of the track without introducing distortion.
- Final Touches: Review your mix and mastering, making any necessary adjustments to achieve a polished and professional sound. Export your track in a high-quality format, such as WAV or AIFF, for distribution.
Collaboration and Sharing
GarageBand offers various options for collaborating on projects with others, making it a versatile tool for musicians and producers. You can share your creations with friends, family, or collaborators to get feedback, refine your work, or simply enjoy the creative process together.
Sharing GarageBand Projects
Sharing your GarageBand projects is a straightforward process. There are multiple methods available, each catering to different needs and preferences.
- Sharing via iCloud: GarageBand allows you to save your projects to iCloud, making them accessible on all your Apple devices. This is a convenient way to work on your project from anywhere, seamlessly switching between your Mac, iPhone, or iPad. The iCloud feature is particularly useful for projects that involve multiple collaborators, as it allows them to access and edit the project simultaneously.
- Exporting as Audio Files: You can export your GarageBand project as an audio file in various formats, including MP3, WAV, and AIFF. This is useful for sharing your finished tracks with others, or for uploading them to music streaming services.
- Sharing via AirDrop: If you’re collaborating with someone nearby, you can use AirDrop to share your GarageBand project quickly and easily. This method is convenient for sharing large files without the need for external storage or cloud services.
- Sharing via Email or Messaging: You can also share your GarageBand project via email or messaging apps, though it’s important to note that file sizes can be large. If you’re sharing a large project, consider compressing it before sending it.
Supported File Formats
GarageBand supports a wide range of file formats, allowing you to import and export audio, MIDI, and other types of data.
- Audio Formats: GarageBand supports common audio formats such as MP3, WAV, AIFF, AAC, and Apple Lossless.
- MIDI Formats: GarageBand can import and export MIDI files in standard MIDI file format (SMF), allowing you to work with MIDI data from other music software.
- Other Formats: GarageBand also supports other file formats, including text files, images, and video files.
GarageBand for Beginners
GarageBand is a powerful and user-friendly music creation software designed for both beginners and experienced musicians. Whether you’re a complete novice or have some musical experience, GarageBand offers a wide range of tools and features to help you create your own music.
Creating Your First Song in GarageBand
This section provides a step-by-step guide to help beginners create their first song in GarageBand.
- Open GarageBand: Launch GarageBand on your Mac or iOS device.
- Choose a Template: Select a template that suits your desired genre, such as “Empty Project,” “Rock,” “Pop,” or “Hip-Hop.” This will provide a basic track structure with instruments and drum loops.
- Add Instruments: Browse the “Instruments” library to find instruments that you want to use in your song. You can add instruments by dragging and dropping them onto the track.
- Record Your Music: Use the “Record” button to start recording your instruments or vocals. You can adjust the recording settings, such as the number of tracks and the recording time.
- Edit Your Music: Once you’ve recorded your music, you can use the editing tools to refine your song. You can trim, copy, paste, and move audio regions, adjust the volume and panning, and apply effects.
- Add Effects: Experiment with different effects to enhance your song. GarageBand offers a wide variety of effects, including reverb, delay, distortion, and equalization.
- Mix Your Song: Use the mixer to balance the levels of your instruments and vocals. You can adjust the volume, panning, and equalization of each track.
- Master Your Song: Once you’re happy with your mix, you can master your song to improve its overall sound. This involves adjusting the overall volume, equalization, and dynamics.
- Share Your Song: When you’re finished, you can share your song with others by exporting it as an audio file or by sharing it online.
Tips and Tricks for Getting Started
Here are some tips and tricks for getting started with GarageBand:
- Explore the Interface: Take some time to familiarize yourself with the GarageBand interface. Experiment with the different tools and features to see what they do.
- Use the Help Menu: If you’re stuck, don’t hesitate to use the Help menu. It provides detailed information about all of GarageBand’s features.
- Watch Tutorials: There are many online tutorials that can teach you how to use GarageBand. Search for “GarageBand tutorials” on YouTube or Google.
- Start Small: Don’t try to create a complex song right away. Start with a simple song and gradually add more instruments and effects as you become more comfortable with GarageBand.
- Have Fun: Most importantly, have fun! GarageBand is a great tool for exploring your creativity and making music.
Resources and Tutorials
Here are some resources and tutorials that can help you learn more about GarageBand:
- Apple GarageBand Website: The official Apple GarageBand website provides comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and support resources. https://www.apple.com/uk/mac/garageband/
- YouTube: YouTube is a great resource for finding GarageBand tutorials. Search for “GarageBand tutorials” or “GarageBand for beginners” to find a wide variety of videos.
- GarageBand Forums: Online forums are a great place to connect with other GarageBand users and get help with specific questions. Search for “GarageBand forums” on Google to find active forums.
Advanced GarageBand Techniques
GarageBand, while user-friendly, offers advanced features for experienced musicians and producers. Beyond basic recording and editing, these techniques unlock a world of creative possibilities, allowing you to shape your music with precision and finesse.
Automation
Automation is a powerful technique that allows you to change parameters of a track over time, creating dynamic and interesting effects. For instance, you can automate volume, panning, effects, and even instrument parameters like filter cutoff or reverb.
- Creating Automation: In GarageBand, select the track you want to automate, then click the “Automation” button in the track header. Choose the parameter you want to automate, and then draw an automation curve in the Automation lane. The curve represents the parameter’s value over time. You can create smooth, gradual changes or sharp, dramatic shifts, depending on your creative vision.
- Automation Examples: Automation can be used for a wide range of effects, including:
- Fading in or out a track
- Creating a build-up or drop in a song
- Adding a subtle movement to a synth or vocal
- Simulating a live performance by adding subtle variations in volume or panning
- Advanced Automation Techniques:
- MIDI Automation: You can automate MIDI parameters like note velocity, pitch bend, and modulation wheel. This allows for expressive control over your MIDI instruments.
- Automation Envelopes: Create complex automation curves with multiple points and slopes. This lets you fine-tune your automation with greater precision.
- Automation Using External Controllers: You can use external controllers like MIDI keyboards or pedal boards to control automation in real-time. This allows for more expressive and dynamic performances.
Scripting
While GarageBand doesn’t offer built-in scripting features, you can utilize AppleScript to automate repetitive tasks or create custom workflows.
- AppleScript Basics: AppleScript is a scripting language that allows you to control applications like GarageBand. You can use it to automate tasks like exporting files, creating new tracks, or applying effects.
- Using AppleScript with GarageBand: To use AppleScript with GarageBand, you’ll need to learn the basic syntax of AppleScript and how to interact with GarageBand’s objects and commands. There are online resources and tutorials available to help you get started.
- Example AppleScript for GarageBand:
tell application "GarageBand"
set the track named "My Track" to selection
set the volume of selection to 0.5
end tell
This script sets the volume of the track named “My Track” to 50%.
Third-Party Plugins
GarageBand offers a range of built-in effects and instruments, but you can expand its capabilities even further by using third-party plugins. These plugins provide additional sounds, effects, and tools that can enhance your music production workflow.
- Plugin Formats: GarageBand supports various plugin formats, including AU (Audio Unit) and VST (Virtual Studio Technology). You can find a wide range of plugins from different developers online.
- Plugin Categories: Third-party plugins cover a wide range of categories, including:
- Instruments: Synthesizers, samplers, drum machines, and more.
- Effects: Reverb, delay, chorus, distortion, EQ, and more.
- Utilities: Tools for analyzing audio, automating tasks, and more.
- Installing Plugins: The process for installing plugins varies depending on the plugin format and your operating system. Most plugins come with installation instructions.
GarageBand Alternatives
GarageBand is a fantastic music production software for beginners, but it may not meet the needs of more experienced musicians or those seeking advanced features. Fortunately, there are many other powerful alternatives available, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
This section will explore some of the most popular GarageBand alternatives, comparing their features, pricing, and suitability for different users. We’ll also discuss how to choose the best music production software for your specific needs.
Popular GarageBand Alternatives
Here’s a list of popular GarageBand alternatives, highlighting their key features and benefits:
- Logic Pro X: Apple’s professional-level music production software. It boasts a vast array of features, including advanced audio and MIDI editing, a comprehensive library of instruments and sounds, and powerful mixing and mastering tools. Logic Pro X is ideal for professional musicians, composers, and producers.
- Ableton Live: A popular choice for electronic music producers and live performers. Its intuitive workflow, session view, and powerful features for manipulating audio and MIDI make it a favorite for creating and performing electronic music. Ableton Live also excels in sampling and beat production.
- FL Studio: A lifetime license-based DAW known for its comprehensive feature set, including a vast library of plugins and instruments. FL Studio is popular for its intuitive workflow, advanced automation features, and powerful step sequencer for creating beats and melodies.
- Studio One: A user-friendly DAW with a focus on ease of use and workflow efficiency. Studio One offers intuitive drag-and-drop functionality, powerful audio editing tools, and a robust sound library. It’s a good choice for beginners and experienced musicians alike.
- Pro Tools: The industry standard for professional audio production. Pro Tools offers an extensive feature set, including advanced audio editing, mixing, and mastering tools. It’s widely used in studios and by professional musicians worldwide.
Choosing the Best Music Production Software
The best music production software for you depends on your individual needs and preferences. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Your experience level: If you’re a beginner, a user-friendly DAW like Studio One or FL Studio might be a good starting point. More experienced musicians may prefer the advanced features of Logic Pro X or Pro Tools.
- Your budget: Some DAWs offer free versions or subscription models, while others require a one-time purchase. Consider your budget and choose a software that fits your financial constraints.
- Your music genre: Different DAWs excel in different genres. For example, Ableton Live is popular for electronic music, while Pro Tools is widely used for recording and mixing audio.
- Your workflow: Consider how you like to work and choose a DAW that aligns with your workflow. Some DAWs are more linear, while others offer more flexibility.
Comparing Features and Pricing
The following table compares the features and pricing of the popular GarageBand alternatives discussed above:
| Software | Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Logic Pro X | Advanced audio and MIDI editing, comprehensive library of instruments and sounds, powerful mixing and mastering tools | One-time purchase: $199.99 |
| Ableton Live | Intuitive workflow, session view, powerful features for manipulating audio and MIDI, excellent for sampling and beat production | Subscription or one-time purchase: $99 – $749 |
| FL Studio | Comprehensive feature set, vast library of plugins and instruments, intuitive workflow, advanced automation features, powerful step sequencer | One-time purchase: $199 – $499 |
| Studio One | User-friendly interface, intuitive drag-and-drop functionality, powerful audio editing tools, robust sound library | Subscription or one-time purchase: $99 – $399 |
| Pro Tools | Extensive feature set, advanced audio editing, mixing, and mastering tools, industry standard | Subscription: $99 – $299 |
Recommendations
Here are some recommendations based on different user profiles:
For beginners: Studio One, FL Studio, or GarageBand (free) are excellent choices due to their user-friendly interfaces and intuitive workflows.
For experienced musicians: Logic Pro X, Ableton Live, or Pro Tools offer a comprehensive feature set and advanced tools for professional music production.
For electronic music producers: Ableton Live is a popular choice due to its session view and powerful features for manipulating audio and MIDI.
For budget-conscious users: FL Studio, Studio One, or GarageBand (free) offer affordable options with excellent feature sets.
Final Thoughts
From its humble beginnings as a simple audio recording tool to its current status as a sophisticated music production suite, GarageBand has become a cornerstone for countless musicians and aspiring producers. Its intuitive interface, comprehensive features, and vast library of sounds have made music creation accessible to a wider audience, fostering creativity and encouraging musical exploration. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your musical journey, GarageBand offers a powerful and inspiring platform to bring your musical vision to life.
GarageBand is a great starting point for music creation, offering a user-friendly interface and a range of instruments. However, for those seeking more professional tools and a wider selection of features, exploring the adobe creative cloud download might be a good next step.
Adobe Audition, part of the Creative Cloud suite, offers advanced audio editing and mixing capabilities that can elevate your GarageBand projects to a whole new level.
