Document management systems, often referred to as DMS, have become indispensable tools for businesses and organizations navigating the digital age. These systems offer a comprehensive solution for storing, managing, and retrieving digital documents, streamlining workflows, and ensuring secure access to vital information.
Table of Contents
From the humble beginnings of paper-based filing systems, document management has evolved dramatically, driven by technological advancements and the increasing volume of digital data. Modern DMS solutions leverage sophisticated technologies like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to provide a robust and efficient platform for managing documents.
Benefits of Implementing a DMS
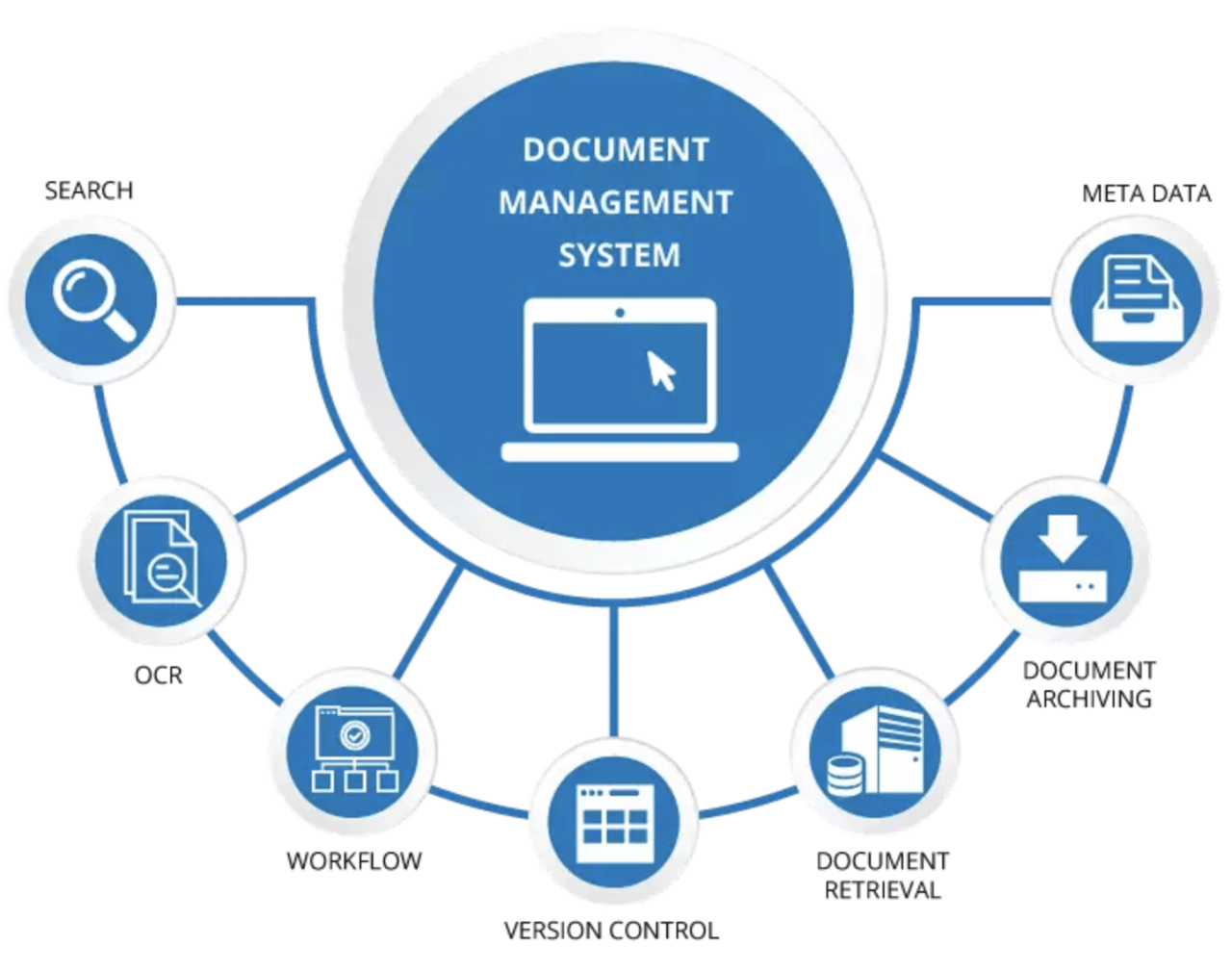
A Document Management System (DMS) can significantly enhance an organization’s operations, offering a plethora of advantages that streamline workflows, improve collaboration, and boost efficiency.
Improved Efficiency
A DMS centralizes all documents in a secure and easily accessible location, eliminating the need for manual searching through physical files or scattered digital folders. This streamlined approach saves time and effort, enabling employees to retrieve documents quickly and efficiently. For instance, a law firm utilizing a DMS can instantly access client files, eliminating the time-consuming process of sifting through physical folders or searching across multiple shared drives.
Enhanced Collaboration
DMS facilitates seamless collaboration among team members, regardless of their physical location. With shared access to documents and version control features, teams can work together efficiently on projects, ensuring everyone has access to the latest information. This eliminates the risk of working on outdated documents or having multiple versions circulating, leading to confusion and errors. For example, a marketing team working on a new campaign can utilize a DMS to share drafts, receive feedback, and track revisions, ensuring everyone is on the same page and the final product is consistent.
Enhanced Security
Security is paramount for any organization, and a DMS provides robust measures to protect sensitive information. Access control features restrict access to documents based on user roles and permissions, ensuring only authorized personnel can view or edit critical data. Encryption safeguards documents from unauthorized access, even if they are lost or stolen. Additionally, DMS platforms often integrate with other security systems, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to create a comprehensive security framework. For instance, a healthcare provider using a DMS can restrict access to patient records to authorized medical staff, ensuring patient privacy and compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Improved Compliance
Organizations operating in regulated industries face stringent compliance requirements. A DMS simplifies compliance efforts by providing tools for document retention, version control, and audit trails. This ensures that organizations can readily demonstrate compliance with regulations and meet audit requirements. For example, a financial institution utilizing a DMS can easily track and retrieve customer records, ensuring compliance with KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations and facilitating audits by regulatory bodies.
Return on Investment, Document management system
The ROI of implementing a DMS is substantial, considering the cost savings and efficiency gains it offers. Reduced paper usage, streamlined workflows, improved collaboration, and reduced risk of data loss are just some of the factors that contribute to a positive ROI. Additionally, the time saved by employees searching for documents can be redirected to more productive tasks, further boosting the overall return on investment. For example, a manufacturing company using a DMS to manage its technical drawings and production plans can expect a significant reduction in errors, improved productivity, and faster product development cycles, resulting in a substantial ROI.
Key Features of a DMS
A Document Management System (DMS) offers a range of features that streamline document processes and improve efficiency. Understanding these features is crucial for selecting a DMS that aligns with your organization’s specific needs.
Document Capture
Document capture is the process of converting physical or digital documents into a format that can be stored and managed electronically. It involves scanning, optical character recognition (OCR), and data extraction.
- Scanning: Physical documents are converted into digital images using scanners.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): OCR software converts scanned images into editable text, making documents searchable and easily processed.
- Data Extraction: Extracting relevant data from documents, such as invoice details or customer information, automates data entry and reduces manual effort.
Document capture ensures that all documents are readily available in a digital format, simplifying storage, retrieval, and sharing.
Document Storage
Document storage involves storing digital documents securely and efficiently. A DMS provides a centralized repository for all documents, making them accessible to authorized users.
- Centralized Storage: A DMS consolidates all documents in a single location, eliminating the need for multiple file servers or physical storage.
- Secure Storage: DMS platforms offer robust security measures, such as access controls, encryption, and data backups, to protect sensitive information.
- Version Control: DMS systems track all versions of a document, ensuring that the most recent version is always accessible. This eliminates confusion and ensures that everyone is working with the latest information.
Document Indexing
Indexing involves assigning s or metadata to documents to facilitate easy retrieval. This makes it possible to quickly find relevant documents based on specific criteria.
- s: Assigning relevant s to documents allows users to search for documents using specific terms.
- Metadata: Adding metadata, such as author, date created, or document type, provides additional information for filtering and searching.
- Automatic Indexing: Some DMS platforms offer automatic indexing, where s and metadata are automatically extracted from documents, reducing manual effort.
Document Retrieval
Document retrieval refers to the process of finding and accessing documents based on specific criteria. A DMS provides powerful search functionalities and filters to streamline this process.
- Advanced Search: DMS platforms allow users to search for documents using s, metadata, or even specific content within the document.
- Filters: Users can filter search results based on various criteria, such as document type, author, date, or location, to narrow down the search and find the required documents quickly.
- Document Preview: DMS systems often allow users to preview documents before opening them, saving time and effort.
Version Control
Version control ensures that all changes made to a document are tracked and managed effectively. This eliminates confusion and ensures that everyone is working with the latest version.
- Document History: DMS platforms maintain a complete history of all document versions, allowing users to track changes and revert to previous versions if necessary.
- Change Tracking: DMS systems can highlight changes made between different versions of a document, making it easy to identify and understand modifications.
- Collaboration Features: Some DMS platforms offer features that allow multiple users to collaborate on documents simultaneously, ensuring that everyone is working on the same version.
Workflow Management
Workflow management automates document-related processes, such as approval workflows, routing, and task assignment. This streamlines operations and improves efficiency.
- Automated Approval Workflows: DMS systems can automate approval processes for documents, such as contracts or invoices, ensuring timely review and approval.
- Document Routing: DMS platforms can automatically route documents to the appropriate individuals or departments based on predefined rules.
- Task Assignment: DMS systems can assign tasks related to documents to specific individuals, ensuring accountability and tracking progress.
Choosing the Right DMS
Selecting a DMS that aligns with your organization’s specific needs is crucial. Consider factors such as:
- Document Volume and Type: The volume and types of documents your organization handles will influence the features you require.
- Security Requirements: The level of security required for your documents will determine the appropriate security features.
- Integration Needs: Consider the need to integrate the DMS with other systems, such as CRM or ERP platforms.
- User Interface and Accessibility: The DMS should have a user-friendly interface and be accessible to all users.
Types of Document Management Systems
Document management systems (DMS) come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and deployment preferences. Understanding these different types is crucial for choosing the right DMS solution for your organization.
Deployment Models
The deployment model refers to how the DMS is accessed and managed. The three main deployment models are on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid.
- On-Premise: This model involves installing and hosting the DMS software on your organization’s own servers. This gives you complete control over the system, including data security and customization. However, it also requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT personnel for maintenance. Examples of on-premise DMS solutions include Alfresco, Documentum, and OpenText.
- Cloud-Based: In this model, the DMS is hosted and managed by a third-party provider in the cloud. This eliminates the need for on-site infrastructure and maintenance, making it a cost-effective option. However, it also means you rely on the third-party provider for security and data availability. Examples of cloud-based DMS solutions include Google Drive, Dropbox, and Microsoft SharePoint.
- Hybrid: This model combines the benefits of both on-premise and cloud-based deployment. Some aspects of the DMS, such as sensitive data, may be stored on-premise, while others, such as collaboration tools, are hosted in the cloud. This provides flexibility and control over data while leveraging the benefits of cloud computing. Examples of hybrid DMS solutions include Box, Egnyte, and Citrix ShareFile.
Functionality
DMS solutions can be categorized based on their functionality, which can range from general-purpose systems to industry-specific solutions.
- General-Purpose: These DMS solutions are designed for a wide range of use cases and can handle various document types. They typically offer core features like document storage, version control, search, and access control. Examples include Adobe Acrobat, Nitro Pro, and PDFelement.
- Industry-Specific: These DMS solutions are tailored to the specific needs of a particular industry, such as healthcare, finance, or legal. They often include features and functionalities specific to the industry’s regulations and workflows. Examples include Epic Systems (healthcare), FIS (finance), and LexisNexis (legal).
Target Audience
DMS solutions are designed for different audiences, from small businesses to large enterprises.
- Small Businesses: Small businesses often require a simple and affordable DMS solution that can handle their basic document management needs. Cloud-based solutions are often preferred due to their low cost and ease of use. Examples include Zoho Docs, Google Drive, and Dropbox.
- Enterprises: Large enterprises often require more robust and scalable DMS solutions that can handle high volumes of documents and complex workflows. On-premise or hybrid solutions are common choices for enterprises, as they offer greater control over data and security. Examples include IBM FileNet, Oracle WebCenter, and Microsoft SharePoint.
Implementing a DMS
Implementing a document management system (DMS) is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. It involves several steps, from assessing your needs to training users and migrating data. A well-planned and executed implementation can yield significant benefits, such as improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced security.
Needs Assessment
The first step in implementing a DMS is to conduct a thorough needs assessment. This involves identifying the specific challenges your organization faces with document management and understanding your requirements for a DMS. It is important to involve stakeholders from various departments to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s needs.
- What types of documents need to be managed?
- What are the current document management processes?
- What are the key challenges and pain points related to document management?
- What are the goals and objectives for implementing a DMS?
- What are the budget constraints?
Vendor Selection
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, you can start evaluating DMS vendors. This involves comparing different vendors based on their features, pricing, and customer support. It is important to choose a vendor that can meet your specific requirements and provide ongoing support.
- Feature Set: Compare the features of different DMS solutions to ensure they align with your needs.
- Pricing: Evaluate pricing models, including subscription fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance.
- Customer Support: Consider the vendor’s reputation for customer service, responsiveness, and technical support.
- Security: Assess the security features of the DMS solution, including data encryption, access control, and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can grow with your organization’s needs and accommodate future growth.
- Integration: Ensure the DMS can integrate with your existing systems, such as your email client, CRM, and ERP.
System Configuration
After selecting a vendor, you need to configure the DMS system to meet your specific requirements. This involves setting up user accounts, defining access permissions, and customizing workflows.
- User Accounts: Create user accounts for all employees who will be using the DMS, assigning appropriate roles and permissions.
- Access Permissions: Define access permissions for different user groups, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive documents.
- Workflows: Configure workflows to automate document approval processes, routing, and other tasks.
- Metadata: Define metadata fields to categorize and search documents effectively.
- Security Settings: Configure security settings, including data encryption, access control, and audit trails.
User Training
User training is essential for a successful DMS implementation. It ensures that employees understand how to use the system effectively and adopt it as part of their daily workflow.
- Onboarding: Provide comprehensive onboarding training for new users.
- Hands-on Training: Offer hands-on training sessions to familiarize users with the system’s features and functionalities.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and resources to users, including user guides, FAQs, and training videos.
- User Feedback: Collect user feedback to identify areas for improvement and ensure the system meets their needs.
Data Migration
The final step in implementing a DMS is data migration. This involves transferring existing documents from your current system to the new DMS.
- Data Preparation: Prepare your existing documents for migration by cleaning up data, removing duplicates, and organizing files.
- Migration Tools: Use migration tools provided by the vendor or third-party solutions to facilitate the data transfer process.
- Testing: Thoroughly test the migrated data to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures during data migration to protect sensitive information.
Best Practices for Successful DMS Implementation
- Define clear goals and objectives: Clearly articulate the desired outcomes of the DMS implementation.
- Involve stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders from different departments to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
- Develop a comprehensive implementation plan: Create a detailed plan that Artikels all steps, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Pilot test the system: Conduct a pilot test with a small group of users to identify and address any issues before full rollout.
- Provide ongoing training and support: Ensure users are adequately trained and have access to ongoing support.
- Monitor and evaluate performance: Regularly monitor the DMS’s performance and collect user feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Common Challenges and Potential Pitfalls
- Resistance to change: Some employees may resist adopting a new system, especially if they are comfortable with the current process.
- Data migration issues: Data migration can be complex and time-consuming, and there is always a risk of data loss or corruption.
- Integration challenges: Integrating the DMS with existing systems can be challenging, requiring careful planning and coordination.
- Lack of user training: Insufficient training can lead to user frustration and low adoption rates.
- Security breaches: Security vulnerabilities can compromise sensitive information, making it crucial to implement robust security measures.
DMS Security and Compliance
A robust Document Management System (DMS) should prioritize data security and compliance with relevant regulations. Implementing appropriate security measures and adhering to industry standards is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining trust with stakeholders.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a fundamental security measure for DMS. It involves converting data into an unreadable format, rendering it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. Encryption safeguards sensitive information during storage, transmission, and access, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms restrict user access to specific documents or system functionalities based on their roles and permissions. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) allows for granular control over data visibility and manipulation. Users should only have access to the information they require for their designated tasks, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access or data manipulation.
Audit Trails
Audit trails provide a comprehensive record of all activities performed within the DMS, including document access, modifications, and deletions. These logs help track user actions, identify potential security breaches, and comply with regulatory requirements for data accountability. Audit trails serve as evidence in case of security incidents or disputes, facilitating investigations and ensuring data integrity.
DMS Compliance
Compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards is paramount for DMS security. Organizations must ensure their DMS adheres to legal frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). These regulations mandate specific data protection practices, including data encryption, access control, and data retention policies.
Security Measures and Compliance Best Practices
- Implement strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance user account security.
- Regularly update software and security patches to address vulnerabilities and maintain system integrity.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify and mitigate potential risks.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures to prevent unauthorized data transfer outside the organization.
- Establish data retention policies that comply with legal requirements and industry standards.
- Provide comprehensive security training to employees, raising awareness about data security best practices and potential threats.
Future Trends in DMS
Document management systems (DMS) are constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain technology is transforming DMS, offering new possibilities and challenges for businesses.
AI and ML in DMS
AI and ML are revolutionizing DMS by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and enhancing user experience.
These technologies enable DMS to:
- Automate document classification and tagging: AI algorithms can analyze document content and automatically categorize them based on s, topics, and other criteria. This eliminates the need for manual tagging, saving time and ensuring consistency.
- Improve search accuracy: ML algorithms can learn from user search patterns and preferences, providing more relevant and accurate search results. This enhances user experience and increases productivity.
- Optimize document workflows: AI can analyze historical data and identify bottlenecks in document workflows, suggesting improvements to streamline processes and reduce turnaround time.
- Detect and prevent fraud: AI-powered anomaly detection algorithms can identify suspicious activities and patterns in document usage, helping to prevent fraud and ensure data security.
Blockchain Technology in DMS
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for managing documents, ensuring their authenticity and integrity.
This technology enables DMS to:
- Ensure document immutability: Blockchain records all document transactions, making it impossible to alter or delete them without leaving a trace. This ensures the authenticity and integrity of documents, crucial for legal and regulatory compliance.
- Enhance document security: Blockchain technology provides a decentralized and secure platform for storing and sharing documents, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Streamline document collaboration: Blockchain enables secure and transparent collaboration on documents, allowing multiple parties to access and modify documents while maintaining a complete audit trail.
- Simplify document verification: Blockchain allows for easy verification of document authenticity and origin, eliminating the need for manual verification processes.
Challenges and Opportunities
While AI, ML, and blockchain technology offer numerous benefits for DMS, they also present challenges and opportunities:
Challenges
- Data privacy and security: Implementing AI and blockchain technology raises concerns about data privacy and security. Businesses must ensure that data is collected, stored, and processed ethically and securely, complying with relevant regulations.
- Integration complexity: Integrating AI, ML, and blockchain technology into existing DMS can be complex and time-consuming, requiring significant technical expertise and resources.
- Cost considerations: Implementing these technologies can be costly, requiring investments in infrastructure, software, and training. Businesses need to carefully evaluate the cost-benefit analysis before adopting these solutions.
Opportunities
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity: AI, ML, and blockchain technology can significantly enhance DMS efficiency and productivity by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and streamlining workflows.
- Improved compliance and risk management: These technologies can help businesses improve compliance with regulatory requirements and reduce risks by ensuring document authenticity, integrity, and security.
- New business opportunities: DMS powered by AI, ML, and blockchain technology can create new business opportunities by enabling innovative solutions and services.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Real-world examples showcase the tangible benefits and challenges of implementing a Document Management System (DMS). These case studies demonstrate how organizations across various industries have successfully leveraged DMS to improve efficiency, enhance collaboration, and streamline their operations.
Case Study: A Healthcare Provider Streamlines Patient Records
This case study focuses on a healthcare provider that faced significant challenges managing patient records. The organization’s paper-based system was inefficient, prone to errors, and hindered patient care. To address these issues, the healthcare provider implemented a DMS.
The DMS solution allowed the organization to:
- Digitize and store patient records electronically, eliminating the need for bulky paper files.
- Improve access to patient information, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Enhance security and compliance by ensuring secure storage and access control for sensitive patient data.
- Reduce administrative overhead and costs associated with managing paper records.
The implementation of the DMS resulted in significant improvements in patient care, increased efficiency, and reduced costs. The organization reported a substantial decrease in the time required to access patient records, leading to improved patient satisfaction and a reduction in medical errors.
Last Word
As we move further into the digital age, the importance of efficient and secure document management only grows. By embracing the power of document management systems, businesses can unlock new levels of productivity, collaboration, and security, ensuring their critical information is readily available, organized, and protected.
A document management system can streamline your workflow, making it easier to organize and access important documents. If you’re looking for a tool to help manage your tax-related paperwork, you might want to check out taxact free , a user-friendly platform designed for individuals and small businesses.
Once you’ve organized your tax documents, a robust document management system can help you track their versions, access them securely, and ensure compliance with regulations.
