ArcGIS, a powerful platform for geographic information systems (GIS), empowers users to explore, analyze, and visualize spatial data. From mapping the urban sprawl of cities to tracking the migration patterns of wildlife, ArcGIS offers a comprehensive suite of tools for understanding our world.
Table of Contents
ArcGIS is a versatile tool used across various industries, including environmental management, urban planning, resource exploration, and even disaster response. Its ability to integrate data from diverse sources, perform complex spatial analysis, and create engaging visualizations makes it an indispensable tool for decision-making in a data-driven world.
ArcGIS for Mapping and Visualization
ArcGIS is a powerful and versatile Geographic Information System (GIS) platform that provides a wide range of tools for mapping, analysis, and visualization of geospatial data. This platform enables users to create, manage, and share maps, data, and applications, providing valuable insights for decision-making in various domains.
Map Types Supported by ArcGIS
ArcGIS supports a variety of map types, each serving specific purposes and visualization needs. Here’s a table showcasing some common map types:
| Map Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Reference Map | Provides general information about geographic features, such as roads, rivers, and boundaries. | A road map showing major highways and cities. |
| Thematic Map | Displays spatial patterns and relationships of a specific theme, such as population density, rainfall distribution, or crime rates. | A choropleth map showing population density by county. |
| Symbol Map | Uses symbols to represent geographic features, such as points, lines, or polygons. | A map showing the locations of schools using different colored markers. |
| Web Map | Interactive maps designed for online viewing and sharing, often incorporating dynamic layers and data. | An interactive map showing real-time traffic conditions. |
| 3D Map | Visualizes geographic data in a three-dimensional space, allowing for more realistic and immersive experiences. | A 3D model of a city showing buildings and terrain. |
Interactive Maps and Dashboards
ArcGIS offers extensive capabilities for creating interactive maps and dashboards, enabling users to explore and analyze data in a dynamic and engaging way.
Interactive maps allow users to zoom, pan, and query data, providing a dynamic and immersive experience. They can incorporate various elements like pop-up windows, legends, and data visualizations, enhancing user engagement and understanding.
Dashboards provide a centralized view of key data and insights, allowing users to monitor trends, track performance, and make informed decisions. They can integrate various data sources, including maps, charts, tables, and gauges, presenting a comprehensive overview of the information.
Data Visualization in ArcGIS
ArcGIS supports various data visualization techniques, allowing users to represent data effectively and convey insights visually.
* Choropleth maps: These maps use color gradients or patterns to represent data values across geographic areas, such as counties or states.
* Proportional Symbol maps: These maps use symbols of varying sizes to represent data values, with larger symbols indicating higher values.
* Dot density maps: These maps use dots to represent individual data points, with the density of dots reflecting the concentration of data.
* Flow maps: These maps depict movement patterns or flows, such as migration patterns or trade routes.
* Heat maps: These maps use color gradients to represent the intensity of data values, with warmer colors indicating higher values.
* Network analysis: This technique analyzes relationships and connections within a network, such as transportation networks or social networks.
ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Pro

ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Pro are two powerful platforms offered by Esri for working with geographic information systems (GIS). While both platforms offer a wide range of capabilities, they cater to different needs and target distinct user groups.
Features Comparison
ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Pro have unique features that cater to specific user needs. The following table highlights key differences between the two platforms:
| Feature | ArcGIS Online | ArcGIS Pro |
|---|---|---|
| Platform | Cloud-based | Desktop application |
| User Interface | Web-based, browser-accessible | Graphical user interface (GUI) |
| Data Storage | Cloud storage | Local storage or network file systems |
| Data Analysis | Limited analytical capabilities | Extensive analytical capabilities |
| Customization | Limited customization options | High level of customization |
| Collaboration | Strong collaboration features | Limited collaboration features |
| Accessibility | Accessible from any device with an internet connection | Requires installation on a local computer |
| Pricing | Subscription-based, with various pricing tiers | One-time purchase or subscription-based |
Use Cases
The choice between ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Pro depends on the specific use case and user requirements.
ArcGIS Online Use Cases
- Web-based mapping and visualization: ArcGIS Online is ideal for creating and sharing interactive maps, dashboards, and stories online.
- Collaborative mapping projects: The platform’s collaborative features allow multiple users to work together on maps and data.
- Data sharing and dissemination: ArcGIS Online provides a platform for publishing and sharing geospatial data with a wider audience.
- Location-based services: It enables the creation of web applications and mobile apps that leverage location data.
- Basic data analysis and visualization: While ArcGIS Online has limited analytical capabilities, it offers tools for basic data exploration and visualization.
ArcGIS Pro Use Cases
- Advanced data analysis and geoprocessing: ArcGIS Pro offers a comprehensive set of tools for complex spatial analysis, data management, and modeling.
- Offline data access and analysis: It allows users to work with data offline, making it suitable for field work or areas with limited internet connectivity.
- Custom map production and design: ArcGIS Pro provides advanced cartographic tools for creating high-quality maps and layouts.
- 3D visualization and analysis: The platform supports 3D data visualization and analysis, enabling the creation of immersive 3D scenes and models.
- Data management and integration: ArcGIS Pro facilitates the management and integration of various geospatial data sources, including raster, vector, and tabular data.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each platform has its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
ArcGIS Online Advantages
- Accessibility: ArcGIS Online is accessible from any device with an internet connection, making it convenient for remote work and collaboration.
- Collaboration: The platform offers strong collaboration features, allowing multiple users to work together on projects.
- Ease of use: ArcGIS Online’s web-based interface is relatively user-friendly, making it accessible to users with varying levels of GIS expertise.
- Cost-effective: Subscription-based pricing makes it a cost-effective option for organizations with limited budgets.
ArcGIS Online Disadvantages
- Limited analytical capabilities: ArcGIS Online has limited analytical capabilities compared to ArcGIS Pro.
- Data storage limitations: Cloud storage may have limitations in terms of data volume and storage space.
- Internet dependency: ArcGIS Online requires an internet connection to access and use the platform.
- Customization limitations: ArcGIS Online offers limited customization options compared to ArcGIS Pro.
ArcGIS Pro Advantages
- Advanced analytical capabilities: ArcGIS Pro provides a comprehensive set of tools for complex spatial analysis and geoprocessing.
- Customization: It offers a high level of customization, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs.
- Offline access: ArcGIS Pro enables offline data access and analysis, making it suitable for field work and areas with limited internet connectivity.
- Advanced cartographic tools: The platform provides advanced tools for creating high-quality maps and layouts.
ArcGIS Pro Disadvantages
- Installation and maintenance: ArcGIS Pro requires installation on a local computer, which can be time-consuming and require system maintenance.
- Higher cost: ArcGIS Pro typically has a higher upfront cost compared to ArcGIS Online.
- Limited collaboration features: Collaboration features in ArcGIS Pro are not as robust as those in ArcGIS Online.
Real-World Applications of ArcGIS
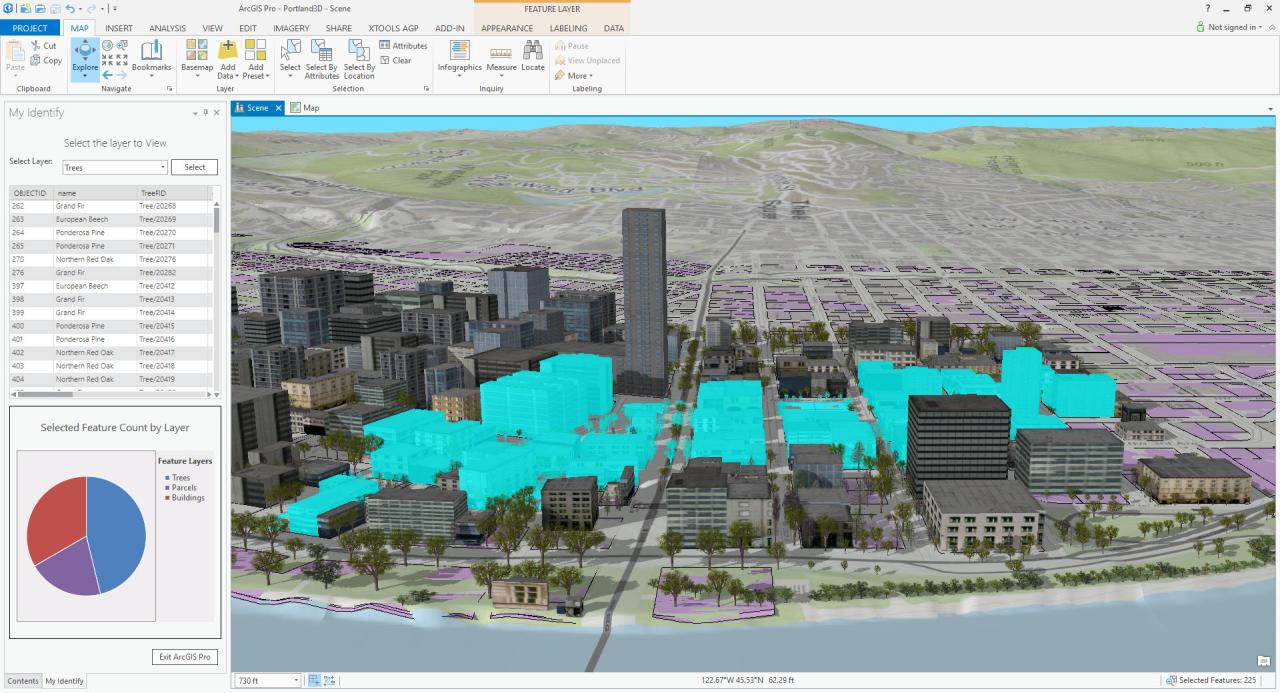
ArcGIS is a powerful tool used across a wide range of industries and applications. Its ability to manage, analyze, and visualize geographic data has revolutionized how we understand and interact with the world around us.
Case Study: Using ArcGIS to Improve Emergency Response in a City
This case study explores how ArcGIS was used to enhance emergency response capabilities in a bustling metropolis. The city faced challenges in coordinating emergency services during natural disasters and other crises. The city’s emergency management team implemented ArcGIS to improve their response efficiency and effectiveness.
Data Collection and Analysis
- ArcGIS was used to create a comprehensive geographic database of critical infrastructure, such as hospitals, fire stations, and evacuation routes. This database incorporated information about building locations, capacities, and accessibility.
- Real-time data from various sources, including weather forecasts, traffic updates, and social media feeds, were integrated into ArcGIS. This provided a dynamic view of the evolving situation during an emergency.
- ArcGIS enabled the team to analyze data and identify potential risks and vulnerabilities within the city. This helped prioritize resources and develop proactive strategies to mitigate potential threats.
Improved Coordination and Communication
- ArcGIS provided a common platform for all emergency responders, including police, fire, and medical services, to share information and coordinate their efforts. This eliminated communication silos and improved collaboration during critical incidents.
- Real-time maps and dashboards created using ArcGIS provided a clear picture of the situation on the ground, enabling responders to make informed decisions and allocate resources efficiently.
- The platform also facilitated communication with the public through interactive maps and alerts, providing timely updates on emergency situations and evacuation procedures.
Impact on Emergency Response
- The implementation of ArcGIS resulted in a significant improvement in response time and efficiency during emergencies. Responders were able to navigate to affected areas more quickly and effectively allocate resources based on real-time data.
- The platform also played a crucial role in improving communication and coordination among responders, leading to a more streamlined and effective response.
- ArcGIS empowered the city’s emergency management team to make data-driven decisions, leading to a more proactive and preventative approach to emergency preparedness.
Closure

As the world becomes increasingly reliant on spatial data, ArcGIS remains at the forefront of innovation, continually evolving to meet the demands of a rapidly changing landscape. With its intuitive interface, robust functionalities, and wide range of applications, ArcGIS empowers individuals and organizations to unlock the power of geospatial information and make informed decisions that shape our future.
ArcGIS is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing geographic data. While it’s primarily used for mapping and spatial analysis, its capabilities extend beyond that. For instance, you can use ArcGIS to track your finances using a dedicated tool like quicken software , which integrates seamlessly with ArcGIS to provide insights into your spending habits and financial performance.
