CAD software, the cornerstone of modern design and engineering, has revolutionized how we create and visualize the world around us. From intricate mechanical components to sprawling architectural masterpieces, CAD software empowers professionals to transform ideas into tangible realities.
Table of Contents
This versatile toolset allows users to create detailed 2D and 3D models, generate precise technical drawings, analyze designs for feasibility and optimization, and even simulate real-world scenarios. The impact of CAD software extends across industries, streamlining workflows, fostering collaboration, and accelerating innovation.
Types of CAD Software
CAD software, or Computer-Aided Design software, has become an indispensable tool across various industries. It enables professionals to create, modify, and analyze designs digitally, leading to improved efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration in the design process.
Industry-Specific CAD Software
CAD software is often tailored to specific industries, catering to their unique design requirements and workflows. Here are some common industry categories:
- Mechanical CAD: This category focuses on designing and analyzing mechanical components, assemblies, and systems. It involves creating 2D and 3D models, simulating mechanical behavior, and generating manufacturing drawings. Popular examples include SolidWorks, Autodesk Inventor, and PTC Creo.
- Architectural CAD: This category is dedicated to designing buildings, structures, and interiors. It involves creating floor plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models, as well as incorporating building information modeling (BIM) functionalities. Popular examples include Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, and Vectorworks.
- Electrical CAD: This category focuses on designing electrical systems, including circuits, wiring diagrams, and layouts. It involves using specialized symbols and components to represent electrical elements and their connections. Popular examples include EPLAN, AutoCAD Electrical, and KiCad.
2D vs. 3D CAD Software
The primary difference between 2D and 3D CAD software lies in the dimensionality of the designs they create.
- 2D CAD Software: This type of software creates designs on a two-dimensional plane, similar to traditional drafting. It’s commonly used for creating technical drawings, floor plans, and schematic diagrams. Examples include AutoCAD, DraftSight, and QCAD.
- 3D CAD Software: This type of software creates designs in a three-dimensional space, allowing for a more realistic representation of objects. It’s widely used for product design, architectural modeling, and engineering analysis. Examples include SolidWorks, Autodesk Inventor, and Rhinoceros 3D.
CAD Software in Different Industries
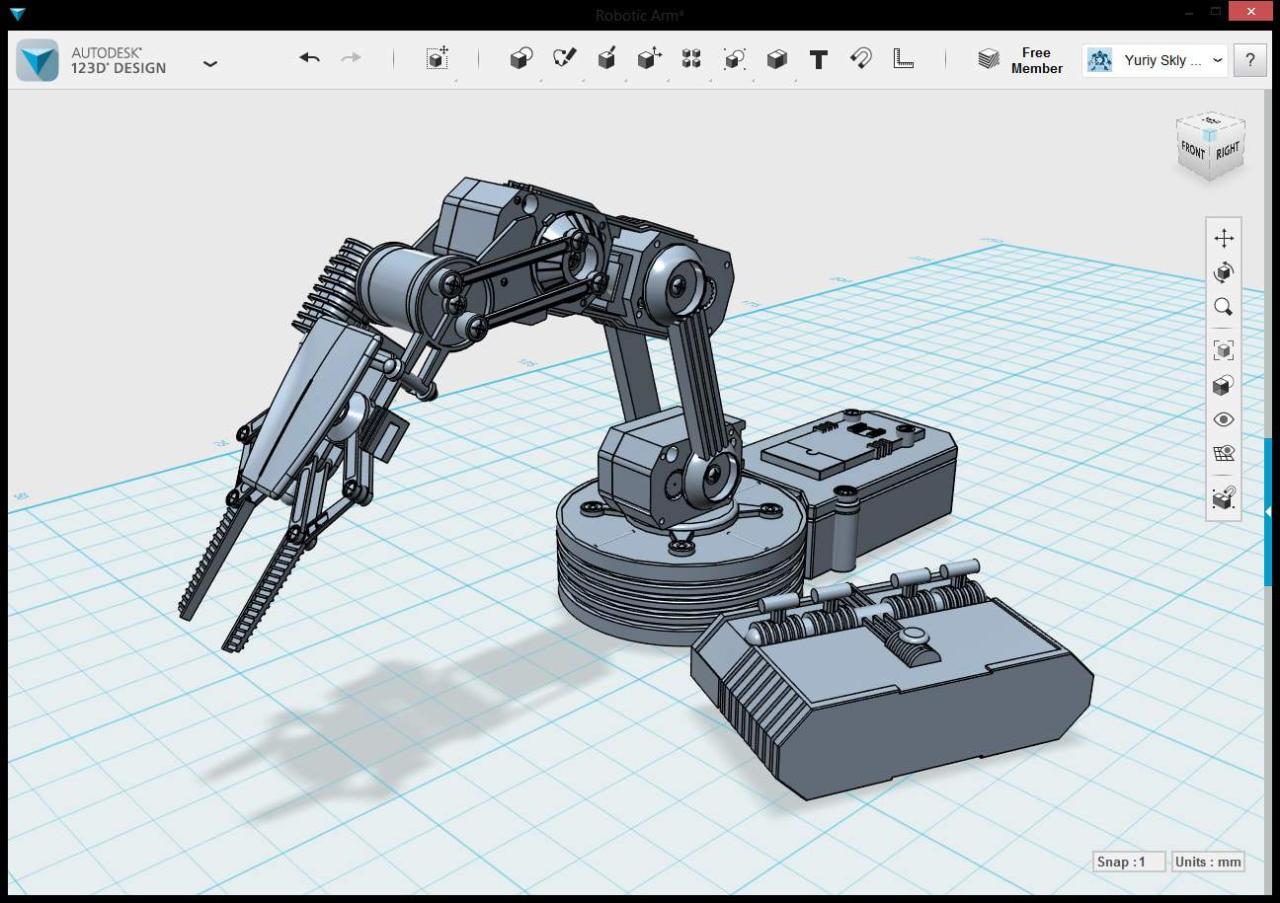
CAD software has become an indispensable tool across various industries, revolutionizing design, engineering, and manufacturing processes. Its applications are vast, ranging from designing intricate mechanical components to creating detailed architectural blueprints.
CAD Software in Mechanical Engineering
CAD software plays a crucial role in mechanical engineering, enabling engineers to design, analyze, and manufacture complex mechanical systems.
- Design and Analysis: CAD software allows engineers to create 3D models of mechanical components and assemblies, facilitating detailed analysis of their performance, stress distribution, and other critical factors. This enables engineers to optimize designs, reduce material usage, and enhance product functionality.
- Manufacturing Process Planning: CAD software provides tools for generating manufacturing drawings, bill of materials, and assembly instructions. This streamlines the manufacturing process, ensuring accurate production and minimizing errors.
- Simulation and Prototyping: CAD software allows engineers to simulate the behavior of mechanical systems under various conditions, such as load, temperature, and vibration. This enables them to identify potential problems early in the design stage, reducing the need for costly physical prototypes.
| Industry | CAD Software Examples | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Engineering | SolidWorks, AutoCAD, Inventor | Design and analysis of mechanical components, assemblies, and systems. |
| Architecture and Construction | Revit, ArchiCAD, SketchUp | Design and documentation of buildings, structures, and interiors. |
| Electrical Engineering | Altium Designer, OrCAD, EAGLE | Design and simulation of electronic circuits and systems. |
| Automotive Industry | CATIA, NX, Creo | Design and development of vehicles, components, and manufacturing processes. |
CAD Software in Architecture and Construction
CAD software is widely used in the architecture and construction industry for designing and documenting buildings, structures, and interiors.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): CAD software like Revit and ArchiCAD facilitates BIM, a process that creates a comprehensive digital model of a building, including its architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems. This allows for better coordination between different disciplines involved in the project, reducing errors and delays.
- Visualization and Rendering: CAD software provides tools for creating photorealistic renderings and virtual walkthroughs of buildings, enabling architects and designers to present their designs to clients in a compelling and immersive way.
- Documentation and Drawings: CAD software generates detailed construction drawings, including floor plans, elevations, sections, and details. These drawings are essential for construction contractors and ensure accurate construction of the building.
CAD Software in Electrical Engineering
CAD software is crucial for electrical engineers, enabling them to design and simulate electronic circuits and systems.
- Circuit Design: CAD software allows engineers to create schematic diagrams of electronic circuits, define component values, and simulate circuit behavior. This helps in verifying circuit functionality and identifying potential problems before physical prototyping.
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Layout: CAD software provides tools for designing and laying out PCBs, ensuring optimal component placement, routing, and signal integrity. This is essential for the efficient and reliable operation of electronic devices.
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD software enables engineers to simulate the performance of electronic circuits under different operating conditions, such as temperature and voltage variations. This allows for optimization of circuit design and identification of potential issues.
CAD Software in the Automotive Industry
CAD software plays a vital role in the automotive industry, enabling the design and development of vehicles, components, and manufacturing processes.
- Vehicle Design: CAD software is used to create 3D models of entire vehicles, including exterior styling, interior design, and mechanical components. This allows for detailed analysis of vehicle aerodynamics, crashworthiness, and other critical factors.
- Component Design: CAD software is used to design individual components, such as engines, transmissions, suspension systems, and safety features. This enables engineers to optimize component performance, reduce weight, and improve manufacturing efficiency.
- Manufacturing Process Planning: CAD software provides tools for generating manufacturing drawings, assembly instructions, and robot programming for automated manufacturing processes. This ensures accurate and efficient production of vehicles and components.
Choosing the Right CAD Software
Choosing the right CAD software is crucial for any professional or hobbyist working with design and engineering. The vast array of options available can be overwhelming, but understanding your specific needs and priorities can simplify the selection process.
Factors to Consider
Several factors influence the choice of CAD software, ensuring it aligns with your project requirements and budget.
- Industry: Different industries have specialized needs. For instance, architects require software with advanced building information modeling (BIM) capabilities, while mechanical engineers prioritize features like finite element analysis (FEA).
- Budget: CAD software ranges from free and open-source options to expensive professional packages. Consider your budget and the features you require.
- Specific Features: Identify the essential features for your work, such as 2D or 3D modeling, rendering, animation, CAM integration, and collaboration tools.
- Ease of Use: Choose software with a user-friendly interface, especially if you are new to CAD. Consider learning curves and available tutorials.
- Operating System Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Support and Documentation: Access to reliable customer support, tutorials, and online communities is vital for troubleshooting and learning new features.
Comparison of Popular CAD Software
A comparison of popular CAD software based on their strengths and weaknesses can help you make an informed decision.
| Software | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Autodesk AutoCAD | Industry-standard software with comprehensive features, excellent compatibility, and a vast user community. | Can be expensive, complex interface, and a steep learning curve. |
| SolidWorks | Powerful 3D modeling software with advanced features for mechanical design, FEA, and simulation. | Can be expensive, requires significant computer resources, and may have a steeper learning curve. |
| Fusion 360 | Cloud-based software with a user-friendly interface, integrated design, and manufacturing capabilities. | Limited offline functionality, potential for slow performance with large files, and ongoing subscription costs. |
| SketchUp | Intuitive and user-friendly software for 3D modeling, ideal for architects, designers, and hobbyists. | Limited advanced features, may not be suitable for complex engineering designs. |
| FreeCAD | Open-source software with a wide range of features, suitable for both 2D and 3D modeling. | Limited support compared to commercial software, may require more technical expertise. |
Evaluating Free and Open-Source CAD Software
Free and open-source CAD software options offer cost-effective alternatives for individuals and small businesses. While they may not have the same feature set as commercial software, they can be suitable for specific projects.
- Feature Set: Assess the software’s capabilities and determine if they meet your project requirements.
- Community Support: Active online communities and forums can provide valuable assistance with troubleshooting and learning resources.
- Documentation and Tutorials: Look for comprehensive documentation and tutorials to help you learn the software.
- Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your operating system and desired file formats.
Learning and Using CAD Software
Learning and effectively using CAD software is crucial for anyone involved in design, engineering, or related fields. It empowers users to create precise and detailed models, drawings, and plans. This section will explore various ways to learn CAD software, emphasize the importance of practice, and provide tips for efficient usage.
Learning CAD Software
Learning CAD software can be achieved through different methods, each catering to different learning styles and preferences.
- Online Courses: Numerous online platforms offer comprehensive courses on various CAD software, providing structured learning with video tutorials, exercises, and assessments. Popular platforms include Coursera, Udemy, and Skillshare. These courses often cover the software’s fundamentals, advanced features, and real-world applications.
- Tutorials: Free online tutorials, often available on YouTube or the software developer’s website, offer step-by-step instructions and demonstrations on specific features and techniques. They are a great resource for quick learning and addressing specific tasks.
- Training Programs: Formal training programs conducted by certified instructors provide in-depth knowledge and practical experience. These programs offer hands-on training, personalized feedback, and industry-specific applications.
- Self-Learning: Self-learning using the software’s built-in tutorials, documentation, and online forums can be effective for individuals who prefer a more independent approach. However, it requires discipline and dedication to explore and master the software’s features.
Practice and Hands-on Experience
Practice is essential for mastering any software, and CAD software is no exception. Consistent hands-on experience helps solidify concepts, develop proficiency, and gain confidence in using the software.
- Start with Simple Projects: Begin with basic exercises and projects to familiarize yourself with the software’s interface and fundamental tools.
- Work on Real-World Projects: Apply your knowledge to real-world projects, whether personal or professional, to gain practical experience and refine your skills.
- Experiment with Different Features: Explore the software’s various features and tools to discover their functionalities and applications.
- Seek Feedback: Share your work with others, such as instructors, colleagues, or online communities, to receive feedback and identify areas for improvement.
Tips for Effective Usage
Effective usage of CAD software involves applying best practices and techniques to maximize efficiency and accuracy in design and engineering tasks.
- Organize Your Work: Establish a clear and organized workflow for your projects, including naming conventions, file management, and layer organization.
- Utilize Templates and Libraries: Leverage pre-designed templates and libraries of objects and symbols to save time and ensure consistency.
- Employ Shortcuts and Macros: Learn and utilize keyboard shortcuts and macros to streamline repetitive tasks and improve efficiency.
- Leverage Collaboration Tools: Utilize cloud-based platforms and collaboration tools to share and work on projects with others seamlessly.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your software and knowledge to benefit from new features, improvements, and industry advancements.
Last Word
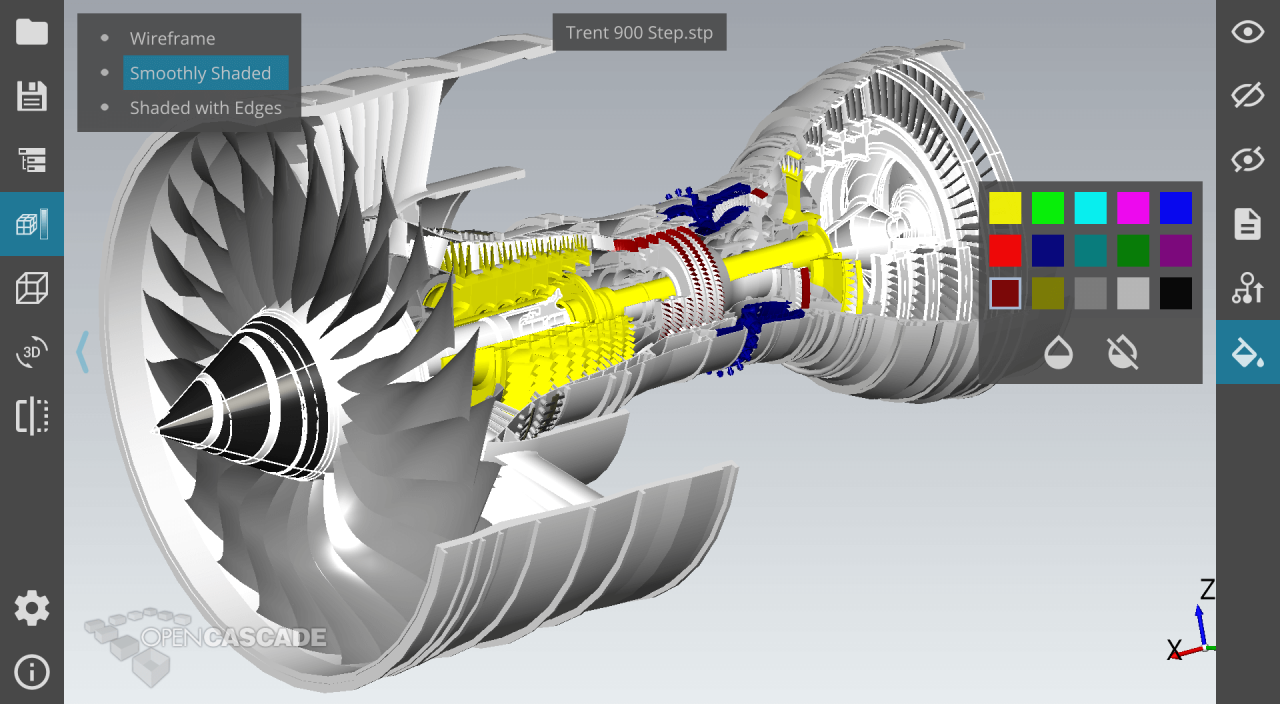
As technology continues to advance, CAD software is poised to play an even more pivotal role in shaping our future. The integration of artificial intelligence, cloud-based solutions, and immersive technologies like virtual and augmented reality promises to further enhance design capabilities, enabling us to push the boundaries of creativity and ingenuity.
CAD software is a powerful tool for creating precise designs, but sometimes you need to access resources that are more securely hidden. For that, you might want to consider using the Tor browser , which helps protect your privacy and security online.
Once you’ve finished your work with the Tor browser, you can return to your CAD software and continue refining your designs.
