Fusion360 – Fusion 360 is a powerful and versatile CAD/CAM/CAE software that empowers engineers, designers, and manufacturers to bring their ideas to life. From conceptual design to production, Fusion 360 provides a comprehensive suite of tools for creating, simulating, and manufacturing products, all within a single, integrated platform.
Table of Contents
This software caters to a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, consumer products, and medical devices. Fusion 360 offers a user-friendly interface and a rich set of features, making it accessible to both beginners and experienced professionals.
Fusion 360 Overview
Fusion 360 is a comprehensive cloud-based software suite that integrates CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) functionalities. It’s designed for engineers, designers, and manufacturers to streamline their product development process, from ideation to production.
Target Audience and Applications
Fusion 360 caters to a wide range of professionals and industries, including:
- Mechanical engineers: Designing and analyzing complex mechanical systems, such as engines, robots, and machinery.
- Product designers: Creating innovative consumer products, ranging from electronics and appliances to furniture and toys.
- Manufacturers: Generating CNC machining paths, optimizing production processes, and simulating manufacturing operations.
- Hobbyists and makers: Developing personal projects, experimenting with 3D printing, and exploring design possibilities.
Key Advantages
- Cloud-based platform: Offers seamless collaboration, data accessibility, and version control.
- Integrated workflow: Combines CAD, CAM, and CAE functionalities in a single environment, simplifying the design-to-manufacturing process.
- User-friendly interface: Provides an intuitive and accessible user experience, suitable for both beginners and experienced users.
- Extensive library of tools: Offers a wide range of tools for modeling, simulation, rendering, and manufacturing.
- Cost-effective solution: Provides a subscription-based pricing model, making it more affordable than traditional CAD software.
Limitations
- Limited offline functionality: Requires an internet connection for most operations.
- Performance limitations: Can experience performance issues with complex models or large assemblies, especially on less powerful computers.
- Learning curve: While user-friendly, mastering the full range of Fusion 360’s functionalities can require time and effort.
- Limited customization: Offers less customization options compared to some specialized CAD software.
Fusion 360 Simulation and Analysis
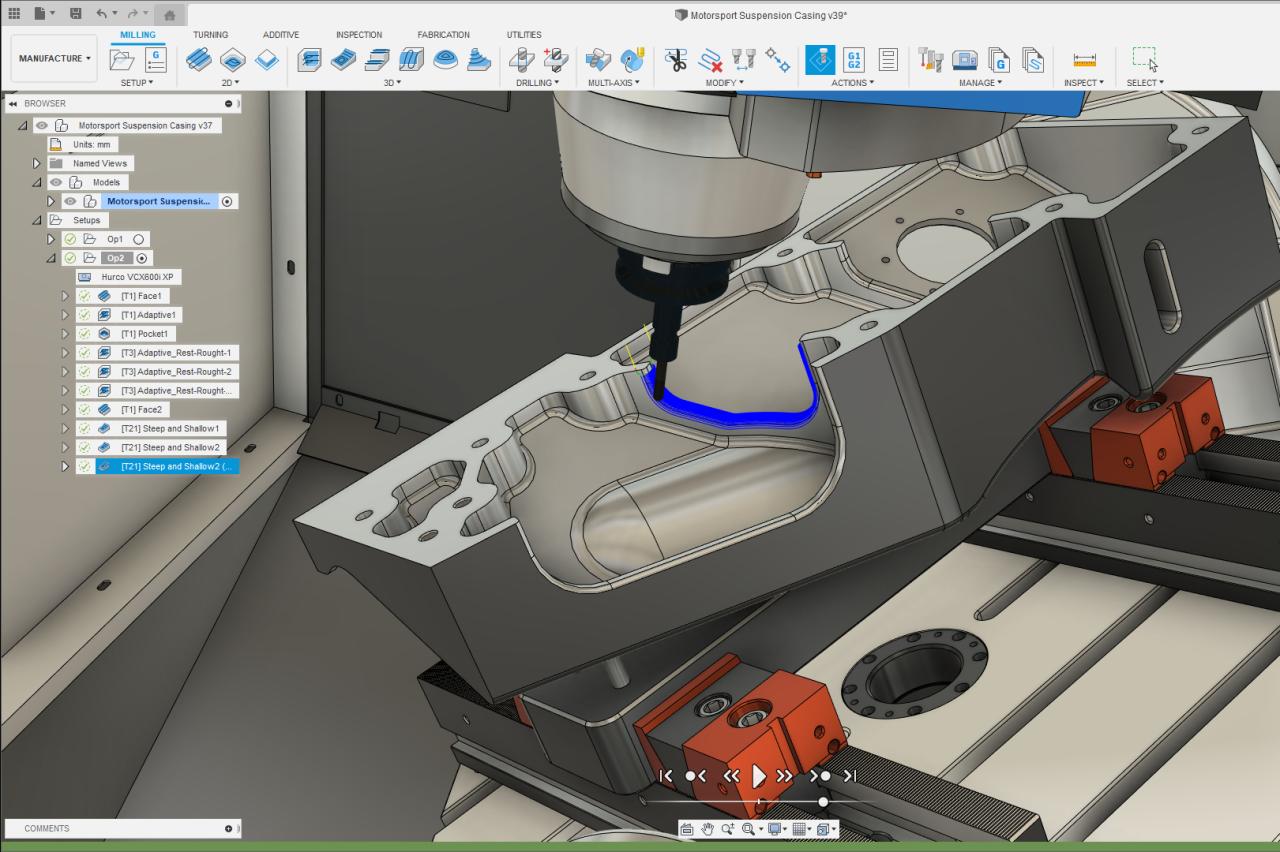
Fusion 360 offers a robust suite of simulation and analysis tools that empower engineers to evaluate the performance and reliability of their designs before physical prototyping. These tools enable users to perform virtual tests, such as stress analysis, thermal analysis, and motion simulation, to gain valuable insights into how their designs will behave under real-world conditions.
Stress Analysis
Stress analysis helps engineers understand how forces are distributed throughout a design, identifying areas that are prone to failure under load. It provides insights into the potential for stress concentrations, fatigue, and fracture.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Fusion 360 uses FEA to divide a design into small elements and analyze the behavior of each element under applied loads. This allows for detailed stress distribution visualization and identification of potential failure points.
- Material Properties: The accuracy of stress analysis results relies heavily on the accuracy of material properties defined for the model. Fusion 360 allows users to specify material properties such as Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio, and yield strength, ensuring realistic simulation results.
- Load Cases: Engineers can define multiple load cases to simulate various scenarios, such as static loads, dynamic loads, and thermal loads. This allows for a comprehensive assessment of the design’s performance under different operating conditions.
Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis helps engineers understand how heat flows through a design and its impact on the overall performance and reliability. It is crucial for designing systems that operate under high temperatures or involve heat transfer.
- Heat Transfer Simulation: Fusion 360 uses computational fluid dynamics (CFD) techniques to simulate heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation. This allows engineers to analyze temperature distributions, heat fluxes, and thermal stresses.
- Convection and Radiation: The simulation accounts for heat transfer through convection, where heat is transferred by the movement of fluids, and radiation, where heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves.
- Heat Sink Design: Engineers can use thermal analysis to optimize the design of heat sinks and cooling systems to effectively dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
Motion Simulation
Motion simulation allows engineers to analyze the dynamic behavior of mechanical systems, such as robots, machines, and mechanisms. It helps in understanding how components interact and move over time.
- Kinematic Analysis: Fusion 360 uses kinematic analysis to simulate the motion of rigid bodies, including their positions, velocities, and accelerations. This allows for the analysis of joint movements, clearances, and interference checks.
- Dynamic Analysis: Fusion 360 can perform dynamic analysis to account for forces, torques, and inertia, providing insights into the forces acting on components and their impact on overall system behavior.
- Mechanism Design: Motion simulation is essential for designing and optimizing mechanisms, ensuring smooth and efficient operation, and preventing potential collisions or interference.
Fusion 360 Industry Applications
Fusion 360 is a powerful and versatile CAD/CAM/CAE software that has become increasingly popular across various industries. Its comprehensive suite of tools allows engineers and designers to streamline their design, simulation, and manufacturing processes, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and product quality.
Automotive Industry, Fusion360
Fusion 360 is widely used in the automotive industry for designing and manufacturing various components, including:
- Vehicle exteriors and interiors
- Engine parts
- Chassis and suspension systems
- Electrical and electronic components
Its advanced capabilities in surface modeling, parametric design, and simulation enable automotive manufacturers to create complex geometries and optimize designs for performance, durability, and weight reduction.
For instance, Tesla Motors has utilized Fusion 360 for designing and developing key components of its electric vehicles, including the Model S and Model X. The software’s integrated simulation tools helped Tesla engineers optimize the aerodynamics and structural integrity of these vehicles.
Aerospace Industry
Fusion 360 is also finding its place in the aerospace industry, where its capabilities in complex geometry modeling and lightweight design are highly valued. It is used for designing and manufacturing components such as:
- Aircraft wings and fuselages
- Engine parts
- Satellite components
- Spacecraft structures
The software’s ability to handle complex surfaces and intricate details is crucial for creating aerodynamically efficient and lightweight aerospace components.
For example, Airbus, a leading aircraft manufacturer, has implemented Fusion 360 to streamline its design and manufacturing processes. The software has helped Airbus engineers create complex geometries for aircraft components, leading to improved performance and reduced weight.
Consumer Products Industry
Fusion 360 is widely used in the consumer products industry for designing and manufacturing a wide range of products, including:
- Electronics
- Household appliances
- Toys
- Sporting goods
Its user-friendly interface and powerful design tools allow product designers to create innovative and aesthetically pleasing products quickly and efficiently.
For instance, GoPro, a leading manufacturer of action cameras, has used Fusion 360 to design and develop its iconic cameras. The software’s advanced modeling capabilities allowed GoPro engineers to create the compact and rugged designs that have made GoPro cameras popular worldwide.
Medical Devices Industry
Fusion 360 is gaining traction in the medical devices industry, where its precision modeling and simulation capabilities are crucial for developing safe and effective medical devices. It is used for designing and manufacturing components such as:
- Prosthetics
- Implants
- Surgical instruments
- Diagnostic devices
The software’s ability to handle complex geometries and perform detailed simulations ensures that medical devices meet stringent safety and performance standards.
For example, Zimmer Biomet, a leading medical device company, has implemented Fusion 360 for designing and manufacturing hip and knee implants. The software’s advanced modeling and simulation capabilities have helped Zimmer Biomet engineers create implants that are both durable and biocompatible.
Final Thoughts: Fusion360
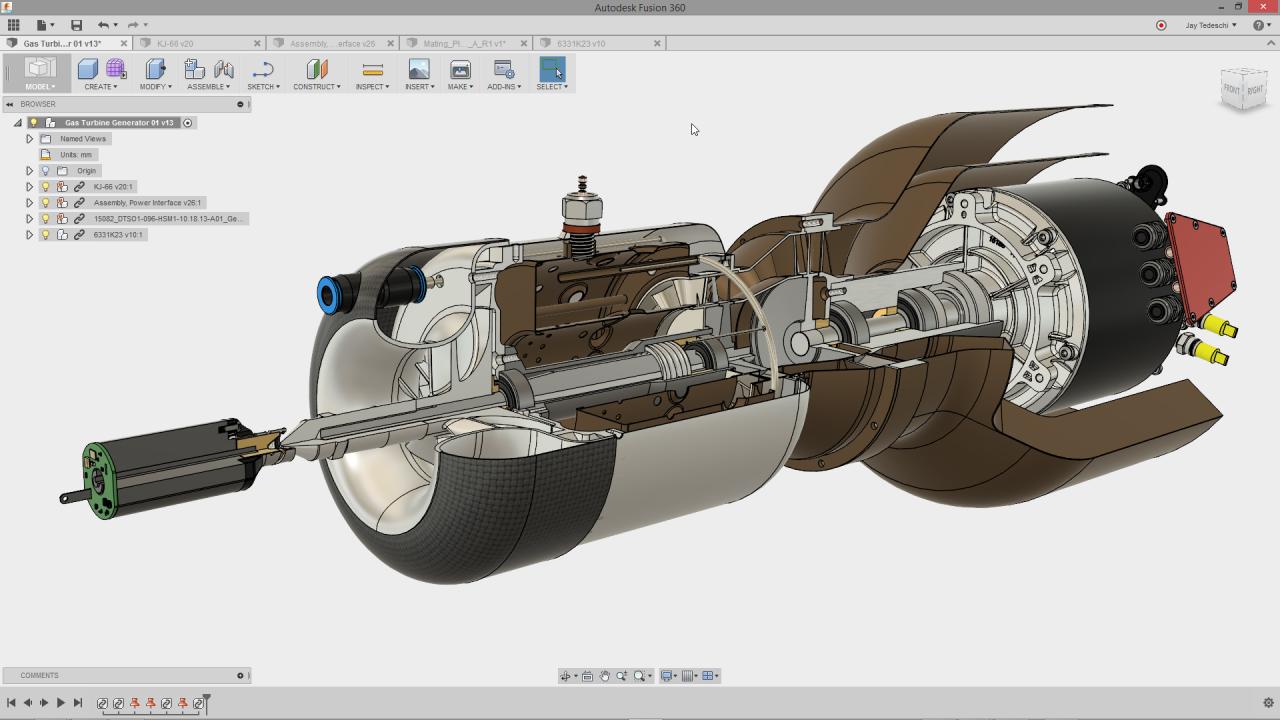
Fusion 360 has revolutionized the way products are designed and manufactured, enabling faster prototyping, improved collaboration, and enhanced product performance. Its intuitive interface, powerful capabilities, and robust community support make it an indispensable tool for anyone involved in the product development process.
Fusion360 is a powerful tool for 3D modeling and design, but sometimes you need a visual aid for communicating your ideas. That’s where a diagramming tool like microsoft visio comes in handy. It allows you to create professional-looking flowcharts, diagrams, and schematics to illustrate complex concepts, making it easier to explain your Fusion360 designs to clients or colleagues.
