3ds Max, a powerhouse in the realm of 3D modeling and animation, has revolutionized the way we create and visualize the world around us. From its humble beginnings, 3ds Max has evolved into a comprehensive software suite that empowers artists, designers, and engineers to bring their ideas to life with unparalleled detail and realism.
Table of Contents
This software, developed by Autodesk, offers a wide range of tools and features for modeling, texturing, lighting, animation, and rendering. Its versatility has made it a staple in various industries, including film and television, game development, architecture, and product design.
Introduction to 3ds Max
3ds Max, a powerful 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software, has been a mainstay in the visual effects, animation, and design industries for decades. Its history is intertwined with the evolution of computer graphics technology, and its features continue to adapt to the demands of modern creative workflows.
History and Evolution of 3ds Max
3ds Max traces its roots back to 1990 when it was initially released as 3D Studio DOS, developed by Autodesk. This early version was a command-line interface-based software that was primarily used for architectural visualization and product design. In 1994, Autodesk released 3D Studio MAX, which introduced a graphical user interface (GUI) and enhanced modeling and animation capabilities. Over the years, 3ds Max has undergone significant updates and improvements, incorporating new technologies and features, including advanced rendering engines, physically based materials, and integrated animation tools.
Core Features and Functionalities of 3ds Max
3ds Max provides a comprehensive suite of tools for 3D modeling, animation, rendering, and visual effects.
- Modeling: 3ds Max offers a variety of tools for creating complex 3D models, including polygon modeling, NURBS modeling, and subdivision surface modeling. Users can create organic shapes, hard-surface objects, and detailed environments.
- Animation: 3ds Max’s animation tools enable users to bring their models to life. It includes keyframing, motion capture, and procedural animation systems, allowing for realistic and dynamic movement.
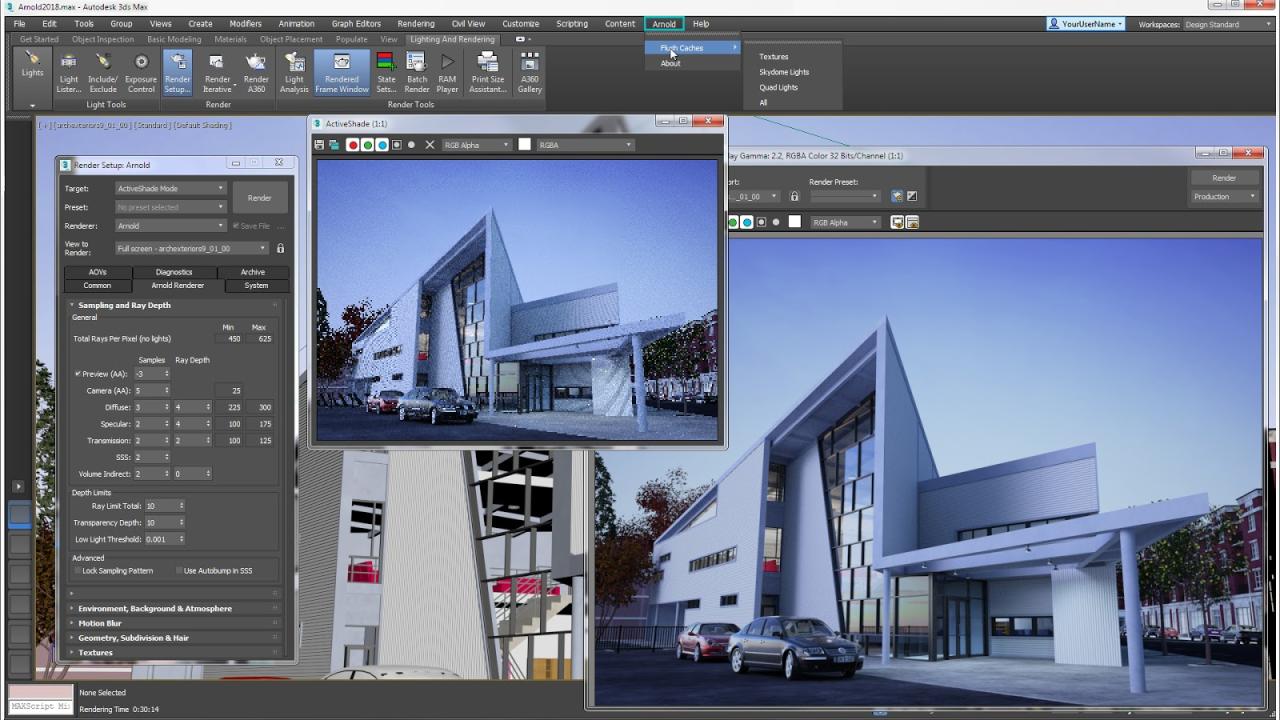
- Rendering: 3ds Max features powerful rendering engines, such as Arnold and V-Ray, that generate photorealistic images and animations. Users can customize lighting, materials, and effects to achieve desired visual styles.
- Visual Effects: 3ds Max integrates tools for creating visual effects, including particle systems, dynamics simulations, and compositing capabilities. These tools are widely used in film, television, and video game production.
Industries and Applications of 3ds Max
3ds Max is widely used across various industries, including:
- Film and Television: 3ds Max is a staple in visual effects production for film and television. It is used to create environments, characters, and special effects. Examples include the visual effects in blockbuster movies like “Avatar” and “Avengers: Endgame.”
- Video Games: 3ds Max is a popular tool for creating game assets, environments, and characters. Its versatility and performance make it suitable for both large-scale and indie game development.
- Architecture and Design: 3ds Max is used by architects and designers to create photorealistic visualizations of buildings, interiors, and product designs. It allows them to present their ideas to clients in a compelling and immersive way.
- Advertising and Marketing: 3ds Max is used in advertising and marketing to create stunning visuals for commercials, product demonstrations, and online campaigns. Its ability to generate high-quality renders and animations makes it an ideal tool for visual storytelling.
Modeling and Geometry
In 3ds Max, modeling is the process of creating 3D objects. It involves defining the shape, size, and details of an object using various tools and techniques. 3ds Max offers a range of modeling methods, each with its strengths and limitations, allowing artists to choose the most suitable approach for their specific needs.
Polygonal Modeling, 3ds max
Polygonal modeling is a fundamental technique in 3ds Max, based on creating objects from polygons. Polygons are simple geometric shapes with three or more sides. By combining and manipulating these polygons, artists can construct complex and detailed models.
- Vertex, Edge, and Face: Polygonal modeling involves manipulating vertices (points), edges (lines connecting vertices), and faces (polygons). By moving, adding, deleting, or subdividing these elements, artists can sculpt and refine their models.
- Extrude and Bevel: Common tools like extrude and bevel are used to create depth and detail. Extrusion pushes a face along a specified direction, while beveling creates rounded edges and corners.
- Modifiers: Modifiers in 3ds Max can enhance and manipulate the geometry of objects. They offer a non-destructive approach to modeling, allowing for easy adjustments and experimentation.
NURBS Modeling
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) modeling provides a more mathematically precise approach to creating smooth, curved surfaces. NURBS curves and surfaces are defined by control points, allowing for greater control over the shape and form of the object.
- Control Points: NURBS curves and surfaces are defined by control points, which influence the shape of the object. By manipulating these control points, artists can create smooth, organic shapes.
- Degree and Knots: The degree of a NURBS curve or surface determines its smoothness. Higher degrees result in smoother curves, while knots control the continuity of the curve.
- Modifiers: Similar to polygonal modeling, modifiers can be applied to NURBS objects to further refine their shapes. Examples include the “NURBS Surface” modifier for creating complex surfaces and the “Loft” modifier for generating surfaces from a series of curves.
Subdivision Surface Modeling
Subdivision surface modeling combines the efficiency of polygonal modeling with the smoothness of NURBS modeling. It starts with a low-resolution polygonal mesh, which is then subdivided into a denser mesh, creating smoother surfaces.
- Base Mesh: Subdivision surface modeling begins with a low-resolution base mesh, often referred to as a “cage.” This base mesh defines the overall shape of the object.
- Subdivision Levels: Subdivision levels determine the density of the final mesh. Higher levels result in smoother and more detailed surfaces.
- Modifiers: 3ds Max offers a variety of subdivision surface modifiers, including “MeshSmooth” and “TurboSmooth.” These modifiers allow for precise control over the subdivision process and the resulting surface smoothness.
Creating a 3D Model: A Chair
To demonstrate the modeling process, let’s create a simple chair using polygonal modeling techniques.
- Create a Base Shape: Start by creating a basic rectangular shape for the chair seat using the “Create” menu > “Shapes” > “Rectangle.”
- Extrude the Seat: Use the “Extrude” modifier to create the thickness of the seat. Adjust the extrusion height to create the desired depth.
- Add Legs: Create four cylinders for the chair legs using the “Create” menu > “Shapes” > “Cylinder.” Position them appropriately beneath the seat.
- Connect the Legs: Use the “Attach” command to connect the legs to the seat, forming a single object.
- Add Backrest: Create a rectangular shape for the backrest and position it behind the seat. Extrude it to create its thickness.
- Refine and Detail: Use tools like “Edit Poly” to adjust the chair’s geometry, adding details like rounded edges and a slight curve to the backrest.
- Apply Materials: Apply materials to the chair to give it a realistic appearance. Use the “Material Editor” to choose colors, textures, and other properties.
Materials and Texturing
Materials are essential for creating realistic and visually appealing 3D models. They define the surface properties of objects, such as color, texture, and reflectivity, influencing how light interacts with them.
Procedural Textures
Procedural textures are generated mathematically within 3ds Max, providing endless possibilities for creating unique and intricate patterns. They are often used for creating repeating patterns, gradients, and abstract textures.
Procedural textures are generated by mathematical algorithms, enabling you to create unique and complex patterns without relying on external image files.
For example, the “Noise” procedural texture can create a variety of organic and chaotic patterns, while the “Checker” texture creates a simple repeating grid pattern.
Bitmap Textures
Bitmap textures are images loaded into 3ds Max, typically in formats like JPG, PNG, or TIFF. They are used to add realism and detail to models, often capturing the appearance of real-world surfaces like wood, stone, or fabric.
Bitmap textures are images used to enhance the visual realism of models, capturing the appearance of real-world materials.
For example, a high-resolution photograph of a wooden plank can be used as a bitmap texture to create a realistic wooden surface.
Image-Based Textures
Image-based textures (IBTs) utilize photographs to create realistic environments and materials. They capture the lighting and reflections of a real-world scene, allowing for highly realistic rendering results.
Image-based textures (IBTs) use photographs to simulate real-world lighting and reflections, enhancing the realism of rendered scenes.
IBTs can be used to create realistic skyboxes, reflecting the colors and patterns of the real-world environment.
Applying Materials and Textures
To apply materials and textures in 3ds Max, follow these steps:
1. Create a material: Create a new material by clicking “Create” > “Materials” > “Standard.”
2. Assign a texture: Select the “Diffuse” map slot in the material editor and choose a procedural, bitmap, or IBT texture.
3. Adjust texture properties: Modify the texture’s parameters to fine-tune its appearance, such as color, scale, and rotation.
4. Apply the material to the model: Select the model and drag the material from the material editor to the model’s viewport.
Lighting and Rendering
Lighting and rendering are crucial aspects of 3ds Max that transform a basic 3D model into a realistic and visually appealing scene. Lighting creates the mood and atmosphere of the scene, while rendering brings the scene to life by generating an image from the 3D model.
Types of Lights
3ds Max offers a variety of light types to simulate different lighting scenarios. Each light type has unique properties that affect the way it illuminates the scene.
- Point Lights: Point lights emit light equally in all directions, simulating a light bulb or a small, concentrated light source. They are often used to create ambient lighting or highlight specific objects.
- Directional Lights: Directional lights emit light from a single direction, mimicking the sun or a distant light source. They are typically used to create a sense of depth and direction in the scene.
- Spot Lights: Spot lights emit light in a cone-shaped beam, simulating a spotlight or a flashlight. They are used to create focused lighting effects, such as highlighting a character or illuminating a specific area.
Global Illumination
Global illumination is a rendering technique that simulates the way light interacts with objects and surfaces in the real world. It takes into account how light bounces off surfaces and casts shadows, creating a more realistic and natural lighting effect. Global illumination techniques can significantly improve the quality of a rendered image, making it appear more lifelike.
Rendering Engines
3ds Max offers several rendering engines, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Scanline Renderer: The Scanline renderer is a traditional rendering engine that is relatively fast and easy to use. It is suitable for simple scenes and quick renders.
- V-Ray: V-Ray is a popular and powerful rendering engine known for its high-quality results and advanced features. It is often used for architectural visualizations, product design, and other complex scenes.
- Corona Renderer: Corona Renderer is another powerful rendering engine that offers a balance of speed and quality. It is known for its ease of use and intuitive interface, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced users.
- Arnold: Arnold is a physically based rendering engine that is often used for film and television productions. It is known for its accurate lighting and realistic materials.
Animation and Motion Graphics
Bringing objects to life and creating engaging visual stories is the essence of animation and motion graphics. 3ds Max provides a comprehensive set of tools and techniques for achieving this, allowing you to create dynamic and captivating visual experiences.
Key Principles of Animation
The 12 principles of animation, established by Disney animators, provide a foundation for creating believable and engaging animation. These principles guide animators in achieving natural motion, expressing emotions, and conveying storytelling elements.
- Squash and Stretch: This principle involves exaggerating the shape of an object to emphasize its movement and weight. For example, a bouncing ball can be squashed on impact and stretched as it rebounds.
- Anticipation: A preparatory action before a major movement, such as a character winding up for a punch, enhances the impact and realism of the animation.
- Staging: Directing the viewer’s attention to the most important element in a scene, using techniques like camera angles, lighting, and character placement.
- Straight Ahead Action and Pose to Pose: These two approaches to animation offer different workflows. Straight ahead action involves animating frame by frame, while pose to pose focuses on key poses and filling in the gaps.
- Follow Through and Overlapping Action: These principles add realism to movements by showing the continuation of motion beyond the main action and allowing different parts of a character to move at different speeds.
- Slow In and Slow Out: This principle creates a smooth transition between movements, emphasizing the beginning and end of an action, making the animation more natural.
- Arc: Most natural movements follow curved paths, adding a sense of fluidity and grace to the animation.
- Exaggeration: Enhancing the movement or expression of a character to make it more interesting and impactful. This can be achieved through exaggerated poses, facial expressions, or movement.
- Timing: The speed and rhythm of the animation, influencing the overall feel and impact of the movement.
- Solid Drawing: This principle emphasizes the three-dimensional nature of objects and characters, ensuring that they appear grounded and believable in the scene.
- Appeal: Creating visually appealing and engaging characters and animations that capture the audience’s attention.
- Secondary Action: Adding subtle movements to enhance the main action, such as a character’s hair swaying in the wind while walking.
Animation Techniques
3ds Max offers a variety of animation techniques, each with its strengths and applications.
Keyframing
Keyframing is a fundamental animation technique that involves setting key poses at specific frames, allowing 3ds Max to interpolate the motion between those poses. This provides a level of control over the animation, enabling the creation of smooth and precise movements.
Motion Capture
Motion capture technology uses sensors to record the movements of an actor or performer, translating those movements into animated data. This technique is commonly used for creating realistic character animations, especially for complex movements like walking, running, or fighting.
Procedural Animation
Procedural animation involves using scripts or expressions to automate the animation process. This technique allows for complex and repetitive animations to be generated automatically, saving time and effort.
Creating a Simple Animation Sequence
To demonstrate the basic principles of animation in 3ds Max, let’s create a simple animation of a bouncing ball.
1. Create a sphere: In the Create panel, select “Sphere” and create a sphere object in the scene.
2. Set keyframes: Go to the Animation menu and select “Create Keyframe.” Set a keyframe for the sphere’s position at frame 1.
3. Move the sphere: Move the sphere to a higher position and set another keyframe at frame 20.
4. Adjust the animation curve: In the Track View, select the sphere’s position track and adjust the animation curve to create a smooth bouncing motion.
5. Add a bounce: Add more keyframes to create a series of bounces, gradually reducing the height of each bounce to simulate realistic physics.
6. Render the animation: Set the animation range and render the sequence to create a video file.
Plugins and Extensions
3ds Max is a powerful 3D modeling and animation software, but its capabilities can be further enhanced with the use of plugins and extensions. These are external tools that add new features, improve workflows, and streamline specific tasks. They allow users to customize 3ds Max to suit their individual needs and project requirements.
Popular Plugins for Specific Tasks
Plugins offer specialized functionalities that can significantly enhance the 3ds Max experience. Here are some popular plugins categorized by their specific uses:
Modeling Plugins
- MeshTools: This plugin provides a wide range of tools for mesh manipulation, including smoothing, subdivision, and edge flow control. It simplifies complex modeling tasks and allows for precise control over mesh geometry.
- PolyTools: PolyTools is a powerful set of tools for manipulating polygon objects. It includes features like polygon selection, edge splitting, and face merging, enabling users to create complex and detailed models.
- RailClone: RailClone is a procedural modeling plugin that allows users to create complex, repetitive geometries based on simple curves or paths. This plugin is particularly useful for creating intricate details, such as fences, railings, or architectural elements.
Rendering Plugins
- V-Ray: V-Ray is a widely used rendering engine known for its realistic and photorealistic rendering capabilities. It offers advanced features like global illumination, physically based materials, and powerful lighting tools.
- Corona Renderer: Corona Renderer is another popular rendering engine that provides a user-friendly interface and efficient rendering performance. It is known for its accurate physical camera simulation and realistic material properties.
- Arnold Renderer: Arnold is a physically based renderer developed by Autodesk. It is renowned for its speed and efficiency, particularly for rendering complex scenes with high polygon counts.
Animation Plugins
- F-Curve Editor Plus: This plugin enhances the functionality of the standard F-Curve editor in 3ds Max. It provides advanced tools for manipulating animation curves, including smoothing, snapping, and interpolation options.
- Pose Editor: Pose Editor is a plugin that simplifies the process of creating and editing character poses. It allows users to quickly adjust multiple bones simultaneously, making character animation more efficient.
- Character Studio: Character Studio is a powerful plugin for creating and animating realistic characters. It includes tools for rigging, skinning, and animating characters, providing a comprehensive solution for character animation.
3ds Max in the Industry
3ds Max has become a cornerstone in various industries, proving its versatility and power in creating stunning visuals and immersive experiences. Its application extends beyond the realm of 3D modeling and animation, influencing the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
Film and Television
3ds Max plays a pivotal role in the film and television industry, where it’s used for a wide range of tasks, including:
* Visual Effects: 3ds Max is instrumental in creating special effects, from realistic explosions and weather phenomena to fantastical creatures and environments.
* Character Animation: The software’s animation tools are used to bring characters to life, with realistic movements and expressions.
* Set Design: 3ds Max enables the creation of virtual sets, allowing filmmakers to visualize scenes before they are physically built.
- Examples: Some notable films that utilized 3ds Max for visual effects include *Avatar*, *The Avengers*, and *Gravity*.
Game Development
3ds Max is a popular choice for game developers, offering a robust set of tools for creating game assets, environments, and characters.
* Level Design: 3ds Max facilitates the design and creation of game levels, from intricate interiors to expansive outdoor landscapes.
* Character Modeling: The software is used to model and animate game characters, giving them realistic appearances and movements.
* Asset Creation: 3ds Max allows for the creation of a wide range of game assets, including weapons, vehicles, and props.
- Examples: Popular games that have employed 3ds Max for game development include *Call of Duty*, *Grand Theft Auto V*, and *The Witcher 3*.
Architectural Visualization
3ds Max is widely used in architectural visualization, providing a powerful tool for creating realistic and immersive representations of buildings and spaces.
* Interior Design: 3ds Max enables architects and designers to visualize interior spaces, showcasing furniture, lighting, and materials.
* Exterior Design: The software allows for the creation of realistic exterior views of buildings, including landscaping and surrounding environments.
* Virtual Tours: 3ds Max facilitates the creation of interactive virtual tours, allowing clients to explore spaces in a realistic and immersive manner.
- Examples: Architectural firms use 3ds Max to create stunning visualizations for projects ranging from residential homes to commercial buildings and urban planning.
Learning Resources and Tutorials
Learning 3ds Max effectively requires access to a variety of resources, including online courses, books, and video tutorials. Each method offers unique advantages and disadvantages, catering to different learning styles and preferences. This section explores various learning resources and their benefits, highlighting specific recommendations for beginners and advanced users.
Online Courses
Online courses provide a structured learning experience with guided lessons, assignments, and often include instructor feedback. They offer flexibility and convenience, allowing learners to study at their own pace and schedule. However, online courses can be expensive, and the quality of instruction can vary significantly.
- Autodesk Learning: Autodesk offers a wide range of online courses for 3ds Max, including introductory, intermediate, and advanced levels. The courses cover various topics, from basic modeling to advanced animation and rendering techniques.
- Pluralsight: Pluralsight provides a comprehensive library of 3ds Max courses taught by industry professionals. The courses are well-structured and include hands-on projects to reinforce learning.
- Udemy: Udemy offers a vast selection of 3ds Max courses at varying price points. The platform features both beginner and advanced courses, covering various topics.
Books
Books provide a more in-depth and comprehensive approach to learning 3ds Max. They often offer detailed explanations, illustrations, and practical examples. However, books can be time-consuming to read and may not be as interactive as online courses or video tutorials.
- “3ds Max for Beginners” by David C. Bohn: This book provides a comprehensive introduction to 3ds Max, covering basic modeling, texturing, lighting, and rendering techniques. It is suitable for beginners with no prior experience in 3D software.
- “3ds Max: The Complete Guide” by Greg Stachowiak: This book offers a more advanced guide to 3ds Max, covering advanced modeling, animation, and rendering techniques. It is suitable for users who have a basic understanding of 3ds Max and are looking to expand their skills.
- “3ds Max: Essential Skills” by Scott Eaton: This book focuses on the essential skills required for creating high-quality 3D models and animations. It covers various topics, including modeling, texturing, lighting, and rendering.
Video Tutorials
Video tutorials offer a visual and interactive learning experience. They are often free and readily available on platforms like YouTube and Vimeo. Video tutorials can be helpful for understanding specific techniques or workflows. However, the quality of video tutorials can vary, and they may not provide a structured learning path.
- CG Cookie: CG Cookie offers a wide range of free and paid video tutorials for 3ds Max. The tutorials cover various topics, from basic modeling to advanced animation and rendering techniques.
- The Gnomon Workshop: The Gnomon Workshop provides high-quality video tutorials taught by industry professionals. The tutorials cover various topics, including modeling, texturing, lighting, rendering, and animation.
- YouTube Channels: Many YouTube channels offer free 3ds Max tutorials. These channels often provide quick tips, tutorials on specific techniques, and project breakdowns.
Recommendations for Beginners
For beginners, starting with a structured online course or a beginner-friendly book is recommended. These resources provide a solid foundation in 3ds Max fundamentals and prepare learners for more advanced topics. Online courses like Autodesk Learning’s “3ds Max Fundamentals” or Pluralsight’s “3ds Max for Beginners” are excellent choices. Books like “3ds Max for Beginners” by David C. Bohn offer a comprehensive introduction to the software.
Recommendations for Advanced Users
Advanced users can benefit from more specialized online courses or books that focus on specific areas of 3ds Max, such as animation, rendering, or scripting. Advanced users may also find value in video tutorials that demonstrate advanced techniques or workflows. Platforms like CG Cookie, The Gnomon Workshop, and YouTube channels specializing in 3ds Max offer a wealth of advanced content.
Final Conclusion: 3ds Max
As we conclude our exploration of 3ds Max, it’s clear that this software continues to be a driving force in the world of 3D creation. Its intuitive interface, robust features, and thriving community make it an ideal tool for both beginners and seasoned professionals. With its vast capabilities and ongoing development, 3ds Max remains at the forefront of innovation, shaping the future of 3D design and animation.
3ds Max is a powerful tool for 3D modeling and animation, offering a wide range of features for creating stunning visuals. However, like any software, it can sometimes encounter performance issues. If you’re experiencing slowdowns or crashes, it might be time to consider optimizing your system.
A system mechanic can help you diagnose and address any underlying problems, ensuring that your 3ds Max projects run smoothly and efficiently.
